Last updated on September 27th, 2023
Nearly 400 million people in the world have diabetes. In addition, it is estimated that 8 million people may be undiagnosed by the disease or are unaware of their health condition [1]. It is therefore essential that we increase awareness regarding diabetes. The first step is to know about the key signs and symptoms of diabetes. This article will give you the correct information about the signs and symptoms of diabetes and how simple lifestyle modifications can help reverse diabetes.

Know About Diabetes
Blood Glucose Action
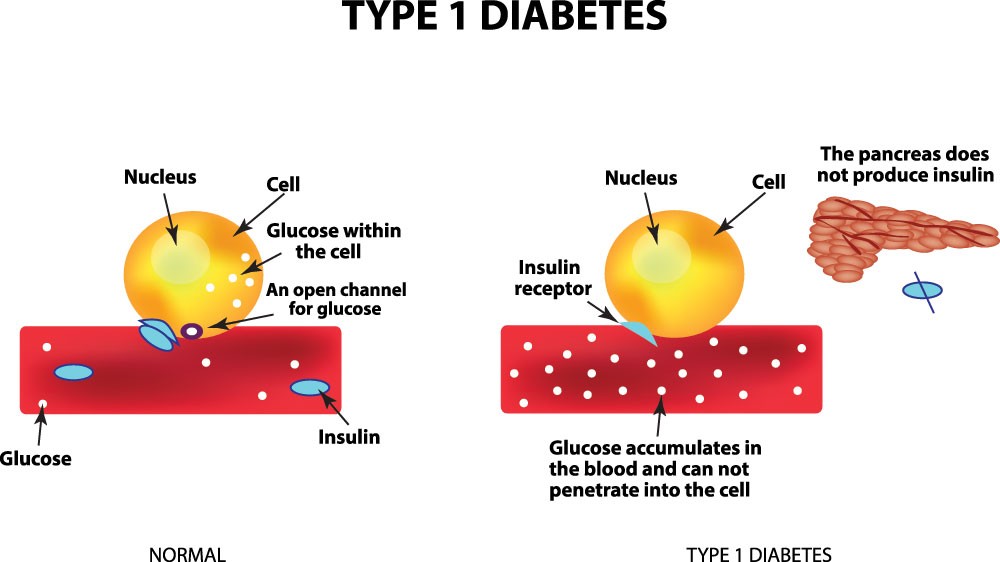
The primary source of energy for our body is glucose. It comes from the diet we take. Insulin is a hormone present in our body that helps absorb glucose by our body cells. Glucose enters the cells with the help of insulin and is further used for energy generation and body metabolism.
Insulin is produced by the pancreas beta cells. But when the pancreas beta cells become weak, or when our body becomes insulin resistant, insulin deficiency occurs. Due to insulin deficiency, the glucose does not reach the cells and stays in our blood. As a result, it causes an increase in blood glucose levels. Insulin Deficiency can be reversed by engaging in physical activities and adopting a nutrient-rich diet.
When the blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels in the body, are too high, it causes diabetes.
Also Read: Blood Sugar Lowering Tips
Normal Blood Sugar Levels:
- 72-99 mg/dl is considered a normal blood sugar level before eating.
- 80-130 mg/dl is considered normal after eating.
Any levels above the given normal blood sugar levels over time are an indication of diabetes.
Read More: Normal Blood Sugar Level Chart
Summary
High blood sugar levels significantly above 140 mg/DL cause diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
The various types of diabetes are as follows:
- Type-1 Diabetes: A chronic condition when your pancreas does not produce enough insulin. It mainly occurs in adolescents.
- Type -2 Diabetes: A condition When your body does not use insulin properly because body cells become insulin resistant. It is more common at the age of 45 and above
- DKA(ketoacidosis diabetes): A severe condition when your body produces excess ketones.
- Gestational Diabetes: It is a condition when the blood sugar levels are high during pregnancy.
Also Read: Are Sugar Free Biscuits Safe for Diabetics?

Symptoms of Diabetes or High Blood Sugar
According to the doctor, there are no apparent signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus, but if symptoms like feeling thirstier, having weight loss, and desire for frequent urination, might be an indication of diabetes.
Type-1 Diabetes
In type -1 diabetes, our immune system attacks the beta cells of our pancreas. As a result, beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas. However, the immune system attacks beta cells and destroys them. As a result, the beta cells of the body become weak. Consequently, they fail to produce enough insulin.
Due to a deficiency of insulin, blood glucose levels are high.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
Type-1 diabetes causes are mainly genetic, wherein the immune system attacks insulin-reducing cells. Exposure to viruses and chemical toxins can also cause type 1 diabetes.
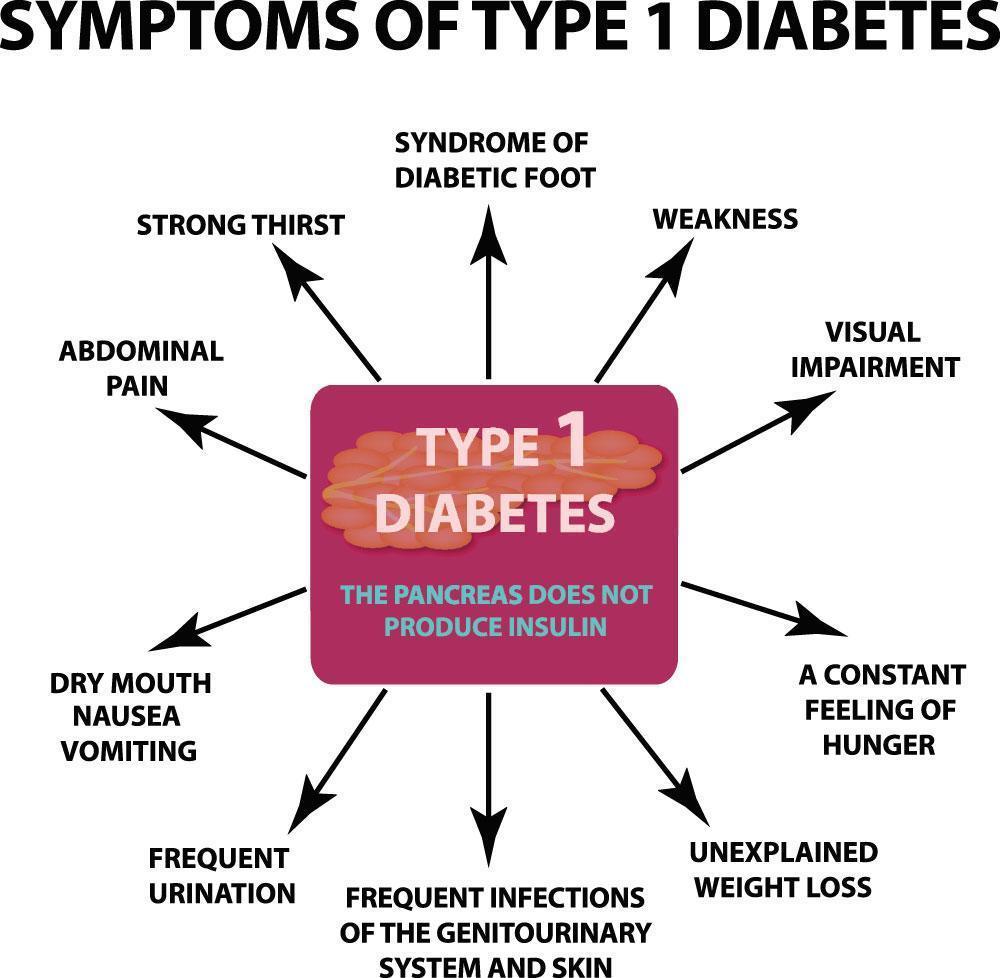
Symptoms of Type-1 Diabetes
- Feeling hungry even after eating
- Fatigue.
- More thirst.
- Mood swings
- Belly pain
- Dehydration
- Weight Loss
Why be Aware of Type-1 Diabetes on Time?
Type-1 Diabetes, if left untreated, can cause any of the following complications:
- Vision loss due to diabetic retinopathy
- Nerve damage foot pain and, in worse cases, leg amputation due to diabetic neuropathy.
- Healing of wounds would become difficult and unbearable due to the slow-healing process.
- Kidney failure due to diabetic neuropathy
- Heart diseases and other heart complications
- Dental problems, you may experience gum bleeding, toothache.
- Mental health problems, especially depression
Thus, it is essential to diagnose type-1 diabetes and get proper treatment to avoid such complications.
Summary
Type-1 blood sugar can lead to serious medical complications. One Should not ignore any signs of increased thirst, increased hunger, and fatigue. They may indicate type-1 diabetes. If you experience any of the above-mentioned symptoms, don’t panic. Type-1 Diabetes can be reversed by following healthy eating, sleeping, and other habits.
Type-2 Diabetes
In type-2 diabetes, the body cells become resistant to insulin. As a result, it decreases glucose absorption by the cells. Glucose thus accumulates in the bloodstream. Over time the high blood glucose levels cause pressure on increasing insulin production and, therefore, weaken the pancreatic cells. Finally, the body is now insulin resistant. Moreover, due to damaged pancreatic cells, the body becomes insulin deficient.
Causes of Type-2 Diabetes
Poor lifestyle, family history, obesity, and age are the leading causes of type 2 diabetes.
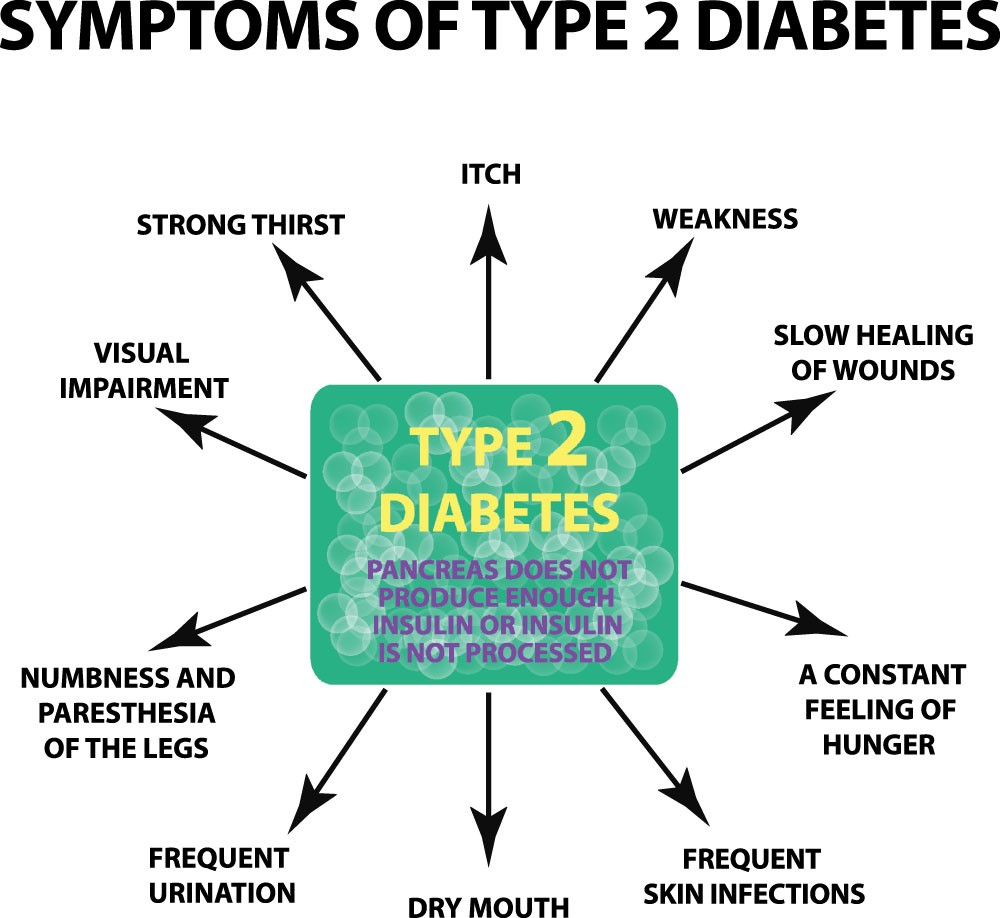
Symptoms of Type -2 Diabetes
- Frequent Infection.
- Slow-healing sores.
- Weight Loss.
- Frequent Urination.
- Extreme Thirst
Chronic Type 2 Blood Sugar Symptoms are:
- Skin infections mainly yeast infections
- Numbness in the feet
- Dark skin patches under armpit, neck, thighs
- Foot pain, slow healing wounds, and nerve damage.
Type 2 Blood Sugar Symptoms in Women
- Painful Urination
- Irregular Periods
- Weight Gain
- Depression
Type 2 Blood Sugar Symptoms in Men
- Skin Infection
- Vision Loss
- Slow Healing Wounds.
- Erectile Dysfunction.
- Frequent Urination.
Also Read: Diabetes and Erectile Dysfucntion
Why be Aware of Type-2 Diabetes on time?
Following are the complications of type 2 diabetes:
- 32 % of people with type 2 diabetes are prone to cardiovascular risks like heart strokes [2]. As a result, they may have life-threatening heart diseases.
- 29% of type 2 diabetic patients have Stage 3 and above kidney damage and diabetic ketoacidosis complications [3].
- Eye damage and loss of vision
- Hearing impairments
- Diabetic neuropathy and nerve damage. These can cause foot ulcers, pain and can lead to leg amputations.
- Memory loss.
- Mood swings. Due to which they are prone to severe depression.
Summary
Type 2 diabetes is mainly due to improper lifestyle, obesity, and family factors. Don’t ignore signs of frequent thirst, frequent urination, numbness, mood swings, and slow healing wounds.
DKA or Diabetic ketoacidosis
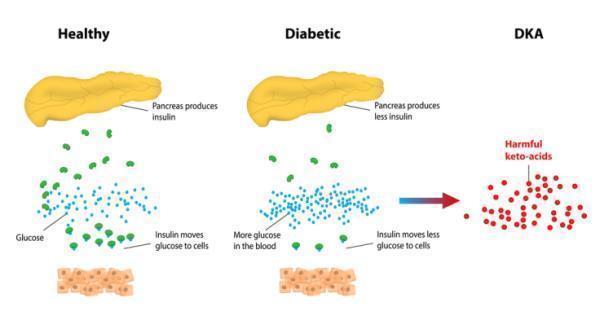
Ketoacidosis diabetes occurs when insulin level gets low, and the body starts to burn fat for energy. DKA is a severe complication of type-1 diabetes. But it can also occur in patients with type 2 diabetes. Due to the low insulin level, extreme ketones produce and cause the blood to become more acidic.
The liver releases ketones after burning body fat for generating energy when insulin is deficient. Therefore, a high level of ketones leads to DKA.
Ketones levels > 1.6 mmol/L for a longer time indicate Diabetic ketoacidosis.
Causes of Diabetic ketoacidosis
Hormone disorders, diuretics and corticosteroids, alcohol consumption, pancreatic, diseases like pneumonia, and urine infection all can trigger DKA.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Symptoms
- High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia)
- High ketone levels in the urine
- Rapid and fruity-smelling breath
- Nausea or Vomiting.
- Muscle Aches.
- Headaches.
- Weakness.
- Belly Pain
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion
Key sign: Having ketone levels in the range of 1.0 to 3.0 or > 3.0 for a longer time.
Why Should You Worry About DKA?
DKA can be a life-threatening condition. It can cause kidney damage and renal failure. If left untreated for a longer time, diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to coma or death.
Summary
High ketones cause diabetic ketoacidosis. It can be life-threatening. Blood tests help in the diagnosis of DKA. You can reverse Diabetic Ketoacidosis through Diabetes Reversal Method where certified health coaches help you by making necessary lifestyle modifications. They push and motivate you throughout the journey, ensuring a healthy life.
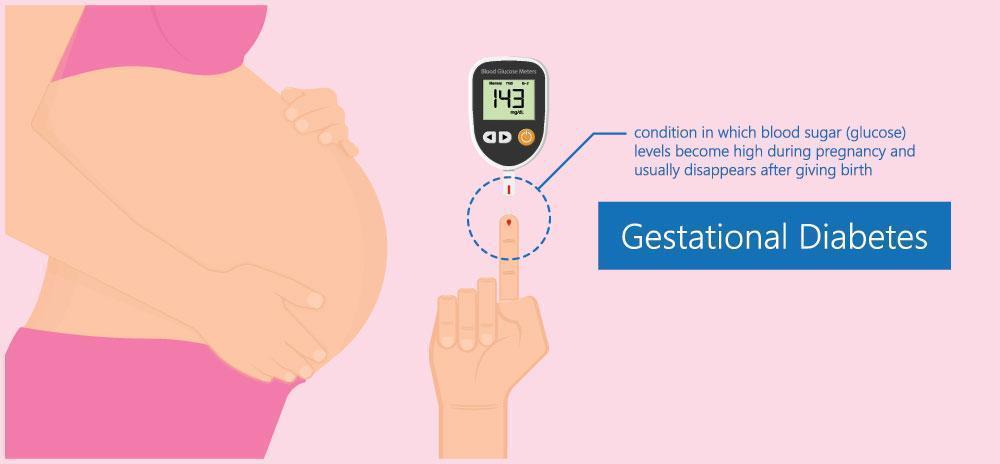
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy in some women when their blood sugar levels go high due to pregnancy.
It usually develops in the 24th week of pregnancy. Thus, doctors recommend blood glucose level tests during 24th to 28th week of pregnancy to rule out or diagnose gestational diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
Weight gain during pregnancy, family history of diabetes, and hormonal changes are the leading causes of Gestational diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
- Weight gain
- Frequent urination
- Unusual thirst
- Sugar in urine
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Skin infection, especially vaginal and bladder infection
Risks Associated With Gestational Diabetes When Left Untreated:
- Mothers who have gestational diabetes are at higher risk of having C-section delivery.
- Women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of delivering an obese baby.
- Gestational diabetes can cause future type 2 diabetes in such women in future. It can thus cause type 2 diabetes complications when left unmanaged.
- Untreated, gestational diabetes can lead to premature delivery and can cause baby death after birth.
- Gestational diabetes, when left unmanaged, can be the cause of breathing problems in babies.
Summary
Eating healthy and doing moderate exercise with proper guidance of experts will help you prevent and cure Gestational Diabetes.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a medical condition where the blood glucose level falls below the normal levels. It is also known as low glucose condition. If left untreated it can lead to severe health problems like coma.
When the blood sugar levels fall below 70mg//dL it is an indication of Hypoglycemia or low sugar levels.
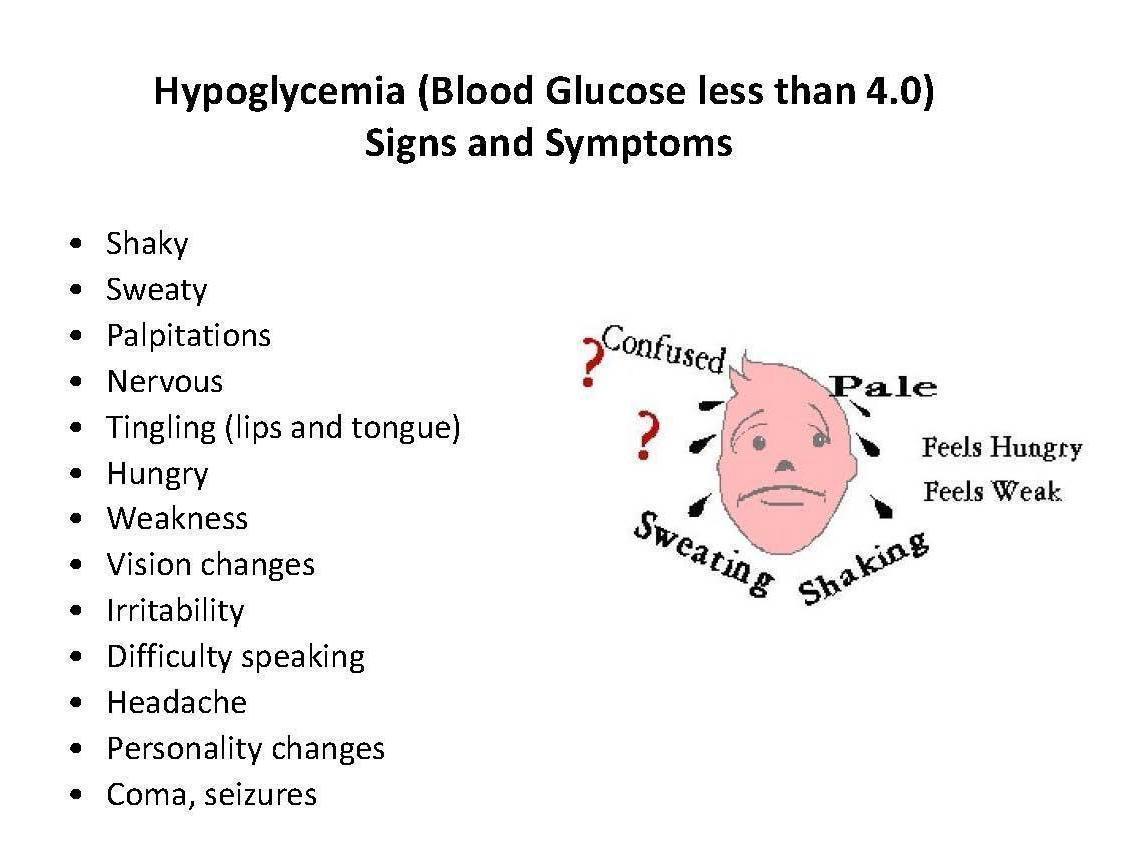
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia are:
- Hunger,
- Disorientation,
- Too much sweating,
- Anxiety,
- Feeling sleepy and dull,
- Sweating,
- Irregular heartbeat,
- Confusion,
- Hand tremor.
This is a serious condition. When left untreated it can lead to seizures and coma. Hypoglycemia is a life-threatening disease. One in every 25 patients suffering from type 1 diabetes dies due to severe hypoglycemia.
Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Eat a few grams (15) of food like a fast-acting carbohydrate. Due to fast-acting carbohydrates, blood glucose levels increase. Consulting a Diet Coach helps you know about fast-acting carbohydrate foods available in your kitchen. Diet Coach also tells the quantity one should consume and how to maintain healthy blood sugar levels throughout life naturally.
Also Read: Best Diabetic Diet Chart
Diagnosis
The following tests help in the diagnosis of type-1 and type-2 Diabetes:
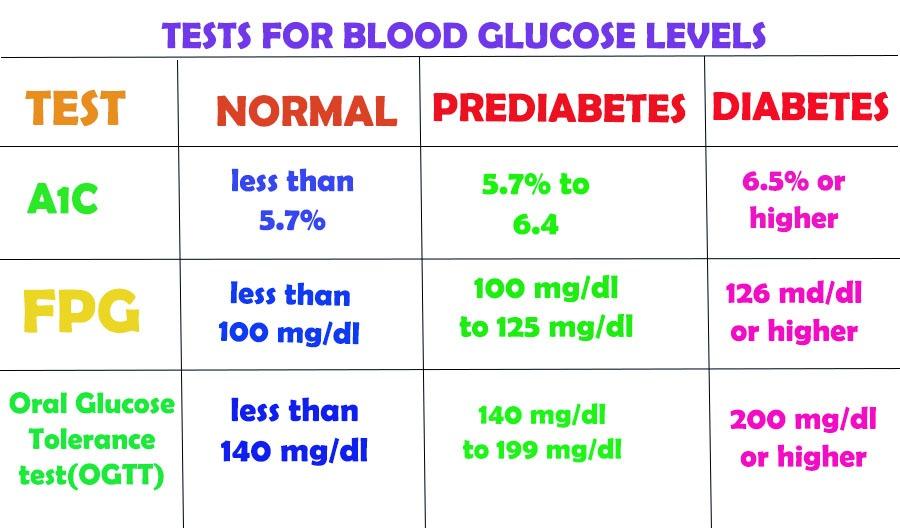
- A1C (Glycated Haemoglobin test): It is a blood test that checks the blood glucose level average for the past three months. If the A1C value > 6.5, it is an indication of diabetes.
- Random blood sugar test: A blood sample can be taken at any time. If the blood sugar value is > 200mg/dL and the patient has signs of frequent urination, thirst, etc., it indicates diabetes.
- Fasting blood sugar test: For this test, a blood sample from the patient is taken after an overnight fast. Blood glucose levels > 126mg/dL indicates diabetes. Generally, these tests are repeated twice or thrice for the confirmation of the diseases.
Read More: Top 10 Best Glucometer In India
Diagnosis of Diabetes Ketoacidosis:
These blood tests check for blood glucose levels, blood acidity levels, and ketones levels.
Blood sugar levels above 200 mm/dL, Ketones levels > 3.0, and high blood acidity levels indicate diabetes Ketoacidosis.
Also Read: Reverse Diabetes Without Medications
Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes
To diagnose gestational diabetes, doctors generally ask for a blood glucose level test. These tests are conducted around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. But if you have a family history of diabetes, doctors may carry out these tests at the early stages of pregnancy.
An oral glucose tolerance test is used to diagnose gestational diabetes. In the oral glucose tolerance test, first, a blood sample is drawn after 1hour of eating. If the blood glucose levels are > 140mg/DL, then a 3-hour test is recommended. Glucose syrup is given, and after 3 hours of taking that glucose syrup, the blood glucose levels are repeated. Any value > 140mg/Dl indicates gestational diabetes.
Doctors shall repeat these tests in the 4th week to confirm gestational diabetes. If the values of the blood glucose levels are still high and > 140 mg/dL, it is diagnosed as gestational diabetes.
Early detection of Diabetes will lead to an early reversal of Diabetes. One should not ignore early symptoms and not hesitate to take expert advice. Health coaches along with Diabetologists will assist you during the Diabetes Reversal Program. Regular follow-ups and weekly challenges without disturbing your daily schedule will help you normalize blood sugar levels in the comfort of your house.
Also Read: Hba1c test full form
Guidelines If You Have Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease that is manageable through proper lifestyle, weight loss programs, diet control, and proper treatment. Some guidelines to help you to manage diabetes efficiently are as follows:
- Test your blood glucose level regularly. You can do this at home through glucometers.
- Maintain a proper diabetic diet chart and a healthy lifestyle.
- Do exercise regularly to manage body weight.
- Take a low-carb diet to maintain proper weight.
- Eat food that is high in fiber. As a result of it, you shall have proper weight management.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
- If you have diabetes, you should cut more oily food from your diet to control weight gain.
- Avoid Smoking.
- Drink lots of water.
- Don’t walk barefoot as it may cause damage to foot skin and cause foot pain and foot ulcers.
- Avoid processed food and juices.
- Avoid Sugary drinks, and sugar syrup as they may cause hyperglycemia.
- Always keep with you an apple or a few raisins if you have complaints of hypoglycemia.
- Measure your sugar levels, especially after workouts, stress, and exercises.
- Don’t ignore any signs or symptoms that can cause complications. As a result, the situation may become life-threatening.
- Don’t take self-medication. Always consult the doctor before taking any medicine. Also, consult a doctor in case of any issues.
- Avoid taking an overdose. Due to this you may create health issues.
Always have emergency numbers highlighted at your home.
Also Read: C-Reactive Protein or CRP Normal Levels Chart For Adults
Bottom Line
Remember, diabetes can be fatal. Therefore, early detection is the key to managing this disease efficiently. Through early detection and proper management, its reversal is possible. Yes, diabetes reversal is attainable through an appropriate lifestyle, medication, diet plan, and positive attitude. So maintain a positive attitude to overcome such challenges.
Also read:- Diabetic patient can eat kiwi fruit?
FAQs:
Are there any signs of uncontrollable or unmanaged Diabetes?
Yes, when Diabetes is left undiagnosed or unmanaged, there are some visible signs. Some of them are bowel problems; the bladder might not be working correctly, the mouth is dry, ulcers and slow-healing wounds, blurred vision, hearing issues, numbness in legs and feet, skin infection, etc.
What will I feel if my blood glucose levels are high?
You shall have an unusual thirst feeling; you have the desire for frequent urination, shortness of breath, and dry mouth.
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes can they have lifelong diabetes?
Generally, after the pregnancy and everyday life returns, women don’t have any issue with Diabetes. But yes, in some cases, it is found that the women with gestational Diabetes had type-2 Diabetes later in their life.
References:
- Saeedi, P., Petersohn, I., Salpea, P., Malanda, B., Karuranga, S., Unwin, N., & IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee. (2019). Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes research and clinical practice, 157, 107843.
- Janjira Jitraknatee, Chidchanok Ruengorn & Surapon Nochaiwong (2020). Prevalence and Risk Factors of Chronic Kidney Disease among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study in Primary Care Practice. Retrieved from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-63443-4
- Thomas R. Einarson, Annabel Acs, Craig Ludwig & Ulrik H. Panton (2018). Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Retrieved from: https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-018-0728-6
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English