Last updated on September 23rd, 2023
In an era where health and wellness have taken centre stage, understanding the intricate aspects of our bodies becomes paramount. In a survey conducted in 2016, there were more than 78 lakh hospitalisations due to diabetes-related complications. Hyperglycemia, a diabetes-related condition, has become increasingly prevalent and demands our attention. This comprehensive blog aims to shed light on hyperglycemia, delving into its hyperglycemia causes, symptoms, complications, hyperglycemia management, treatment and more. Whether you’re personally navigating this condition or seeking knowledge to support a loved one, embark on a journey to grasp the complexities of hyperglycemia and take control of your health. Let’s begin!

Hyperglycemia Meaning
There is much buzz around on the internet as to what is hyperglycemia. So, let’s clear the air in simple words. The simple hyperglycemia definition is when your blood sugar levels are too high. Having hyperglycemia implies you already have diabetes. It usually happens in diabetes patients when their body can’t handle the sugar properly. There are many factors at play here. The factors can be the food you eat, the level of daily physical workouts you do, prevailing illnesses, etc. Not taking diabetes medication or insulin on time or skipping them can also lead to hyperglycemia.
If hyperglycemia goes unattended for long periods, it can cause severe damage to nerves, blood vessels, organs, etc. Severe levels of hyperglycemia can lead to life-threatening conditions like diabetic coma and diabetes-related ketoacidosis. These conditions are more prone to diabetics who are on insulin or people with undiagnosed type 1 diabetes.

Hyperglycemia Range
Type 2 diabetics have increased levels of blood sugar. They go into the hyperglycemia range more easily. Three tests determine hyperglycemia levels, which are as follows:
- Fasting hyperglycemia: For individuals undiagnosed with diabetes having fasting blood sugar greater than 99 mg/dL come in the hyperglycemia range.
- Postprandial hyperglycemia: Postprandial hyperglycemia test is done 2-3 hours after your meals. If the blood glucose is higher than 180 mg/dL, then it is usually considered hyperglycemia.
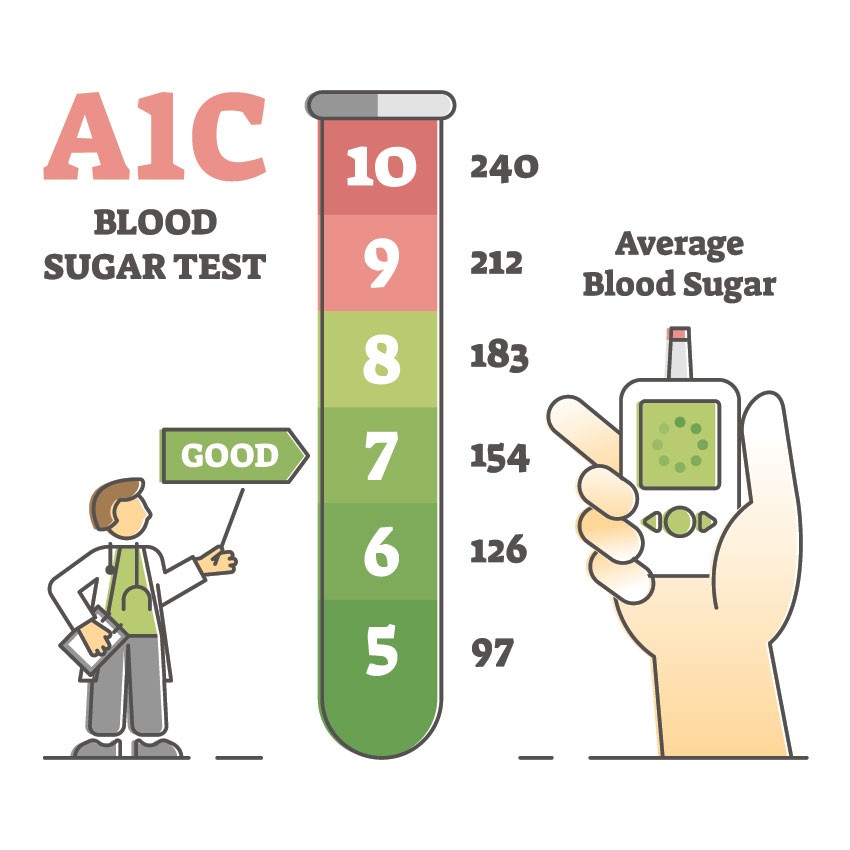
- HbA1c hyperglycemia: HbA1c tells the average blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months. In diabetes patients, normal HbA1c levels are above 6.5%. In hyperglycemia, the HbA1c is on the higher side. Therefore, doctors advise people with hyperglycemia to keep HbA1c around 7%.
Hyperglycemia Symptoms
Hyperglycemia symptoms aren’t visible until your blood sugar reaches high levels. These symptoms are usually visible when blood sugar is above 200-250 mg/dL. Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include the following:
- Increased Thirst (Polydipsia): Elevated blood sugar can make your body drain more fluids through frequent urination, leading to increased thirst.
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): High sugar levels make the kidney’s filtration tough. As of now, there is excess glucose, which results in frequent trips to the restroom.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Cells may not get enough glucose for energy. This happens due to insulin resistance or inadequate insulin. This leads to feelings of tiredness and hyperglycemia dizziness.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can cause some damage to your eye’s lens, leading to temporary blurriness.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Despite high blood sugar, the body’s cells may be starving for energy, leading to increased appetite.
Long-term Diabetic Hyperglycemia Symptoms
Some of the acute hyperglycemia symptoms you can experience in the long term:
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Hyperglycemia can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and injuries, increasing the risk of infections and delayed healing.
- Recurrent Infections: High blood sugar weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections like urinary tract infections and skin infections.
- Weight Loss: In some cases, uncontrolled hyperglycemia can lead to weight loss. In hyperglycemia levels, the body starts breaking down muscle fat to complete its energy requirements.
- Tingling or Numbness: Elevated blood sugar can damage nerves over time, causing a condition called diabetic neuropathy, which can result in tingling, numbness, or pain, typically in the extremities.
- Irritability: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can affect mood, leading to irritability and mood swings.
However, sugar levels at which patients experience these signs and symptoms can vary. Therefore, look for these signs in the early stages. You may also find some signs of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. If hyperglycemia is left unattended, it can progress to diabetes-related ketoacidosis. In this, blood turns acidic due to the absence of insulin and the presence of a high amount of ketones. This further causes coma or death.
Read More: How To Stimulate Your Pancreas to Produce Insulin Hormones in the Body?
Hyperglycemia Causes
Hyperglycemia is the result of a lack of insulin production or absorption in our body. The pancreas is responsible for the production of insulin. However, there are also other factors contributing to hyperglycemia. Excessive cortisol, also known as stress hormone and growth hormone, can also contribute to high blood glucose.
Insulin Resistance
Generally, the main and most common hyperglycemia causes is insulin resistance. Impaired insulin sensitivity is the other name for insulin resistance. This phenomenon happens when muscles, organs, and fat become unresponsive or less responsive to insulin. When insulin resistance happens, your body requires more amount of insulin to regulate blood sugar. Failure to produce enough insulin progresses to hyperglycemia. Therefore, sugar in hyperglycemia blood sugar level is very high. Though insulin resistance is the primary reason for type 2 diabetes, even non-diabetic hyperglycemia can occur. Moreover, insulin resistance can for temporary periods or in permanence.
Some common reasons for insulin resistance:
- Obesity
- Less or no physical workout
- Consumption of foods rich in simple carbs, trans fat, sugar, etc.
- Some medicines for blood pressure, HIV treatment, and a few psychiatric medicines.
Some hormonal ailments can contribute to insulin resistance and make blood sugar reach the hyperglycemia range. These include:
- Excessive cortisol
- Pregnancy
- Growth syndrome or Acromegaly
- Gestational diabetes
Read More: What Is Sliding Scale Insulin Therapy Chart For Diabetics
Pancreas
Pancreas dysfunction can result in less or no insulin production, leading to hyperglycemia. Pancreas can have problems like:
- Chronic Pancreatitis: In this, inflammation is caused in the pancreas, harming the insulin-secreting cells. This condition in the pancreas makes it incapable of secreting insulin, causing hyperglycemia levels.
- Pancreas Cancer: Pancreatic cancer can cause damage to insulin-producing cells. More than 25%-30% of pancreas cancer patients are diagnosed with hyperglycemia prior to detection of pancreas cancer. Diabetes pateints already have 8 times more risk of pancreatic cancer than normal individuals.
- Autoimmune syndrome: This happens in Type 1 diabetes patients. In this immune system attacks the insulin-secreting cells, increasing the blood sugar levels for unspecified reasons.
- Cystic Fibrosis: Patients of this disease develop mucus clogging the pancreatic functions. This results in very little insulin production and gives you hyperglycemia complications.
Causes For Temporary Hyperglycemia
There are some temporary reasons for experiencing hyperglycemia for both diabetics and non-diabetics. A sedentary lifestyle, stress and surgery can temporarily increase your blood sugar and make it reach the hyperglycemia range. Emotional stress releases cortisol or epinephrine in your body, also increasing blood sugar levels. Also, there are some drugs causing hyperglycemia that should be avoided.
Hyperglycemia Causes in Diabetes Patients

Diabetes patients are most prone to the development of hyperglycemia. This can happen especially when you consume unhealthy foods and compromise with diabetes medication. Some reasons include:
- Taking unregulated or irregular dosage of insulin. Also, injection of expired or wrong insulin.
- Consuming refined and processed foods
- Intake of carbs is excessive in comparison to insulin dosage.
- Less or no physical workout
- Dawn phenomenon
Risk Factors of Hyperglycemia
There are some major factors that contribute to hyperglycemia, which include:
- Unregulated eating
- Irregular diabetes checkup
- Illness and surgery
- Not taking proper insulin therapy
- Specific medication
- Stress and anxiety
- Steroids and immunosuppressants
These are the top risk factors that can make your blood sugar reach hyperglycemia levels. You may also require extra insulin or medicines to keep your sugar level in control during illness and stress.
Read More: What is Glycemic Index And To Calculate?
Hyperglycemia Complications

Keeping your blood sugar in hyperglycemia blood sugar level for prolonged periods can give rise to many hyperglycemia complications. This may cause heavy damage and harm to the organs, tissues and blood vessels. Complications which can develop include:
- Heart ailments
- Stroke
- Paralysis attack
- Eye damage or retinopathy
- Nerve damage or neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Gastroparesis
- DKA (Diabetic ketoacidosis) or Hyperglycemia ketoacidosis
- Hyperglycemia seizures
Another important factor that contributes to diabetes or hyperglycemia complications is genetics. Also, the time for which you have had diabetes plays a major role.
Read More: What Is Type 2 Diabetes Management?
Hyperglycemia Diagnosis
Doctors recommend hyperglycemia nursing diagnosis through blood tests. There are three main tests for hyperglycemia diagnosis:
For fasting blood sugar, the recommended blood sugar range for diabetics is between 80 mg/dL and 130 mg/dL. For diabetes patients over 60 years of age and with heart, lung or kidney ailments, the pre hyperglycemia range is 100 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL.
The postprandial blood sugar should be under 180 mg/dL to avoid hyperglycemia complications. These target ranges may change for older patients during pregnancy and organ diseases.
The HbA1c test measures the blood sugar percentage against oxygen-carrying protein in RBCs, also known as haemoglobin. A diabetes patient has HbA1c above 6.5%. However, in hyperglycemia, doctors advised bringing your A1c level to around 7% and then below.
There is also another method known as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). This is a rapid home testing apparatus done using a glucose meter. The device indicates when your blood sugar reaches the hyperglycemia range. However, this method is prone to inaccuracy, so tally readings with traditional blood sugar tests.
Read More: 15 Foods To Lower Blood Sugar Levels
Hyperglycemia Treatment

Hyperglycemia treatment can be done through various hyperglycemia care plans, depending on its severity and the individual’s circumstances. Here are some approaches:
Insulin or Medication
If you have diabetes hyperglycemia, your doctor may prescribe specific insulin and medications to lower your blood sugar levels.
Dietary Changes
Adjusting your diet can help control blood sugar. Focus on low-carb, high-fiber foods, limit sugar intake and take a hyperglycemia diet. Consult a dietitian for personalised suggestions.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity can assist in reducing blood sugar by improving insulin sensitivity. Engage in muscle-building workouts. Muscles absorb sugar from blood and will bring down hyperglycemia blood sugar levels.
Monitoring
Regularly check your blood sugar levels as advised by your doctor and make necessary adjustments as suggested.
Hydration
Drink a good amount of water to help flush excess sugar from your bloodstream. Having hyperglycemia also increases thirst.
Stress Management
Stress can elevate blood sugar levels to hyperglycemia levels. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help manage stress.
Medication Adjustment
If you’re on diabetes medications, your doctor may need to adjust your dosage or switch to a different hyperglycemia medication.
Hospitalisation
Let’s hope it does not come to this, but hospitalisation may be necessary in severe cases of hyperglycemia emergency treatment. Hospitalisation is necessary for intensive recovery with intravenous fluids and insulin.
It’s critical to work closely with your doctor. Follow the medications prescribed, food and hyperglycemia diet plan as designed. to create a tailored treatment plan for hyperglycemia treatment. Do not hesitate to seek medical attention in diabetes vs hyperglycemia. These could be signs of a medical emergency.
Read More: Key Differences Between Diabetologists And Endocrinologists?
Steps You Can Take To Prevent Hyperglycemia
Already having diabetes makes it very difficult to prevent high blood glucose altogether. But sticking with diabetes hyperglycemia can be avoided. Follow a hyperglycemia care plan as a priority. Diabetes and hyperglycemia management is more or less the same. Work closely with your doctor to find out the reason for your blood sugar levels reaching the hyperglycemia range. The reason can be simple, from adjusting the dosage and eating habits to complex organ disorders. Therefore, timely hyperglycemia diagnosis and treatment is advised. Follow can prevent hypoglycemia blood sugar level:
- Taking prescribed medication on time
- Regular blood sugar assessment
- Following diabetes and hyperglycemia diet.
Read More: Best Diabetes Diet Plan – Dietary Guidelines For Diabetic Patients
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperglycemia is a condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, but it can be managed effectively with the right knowledge and tools. We’ve explored its causes, symptoms, complications, and various ways to control and hyperglycemia treatment. Remember that knowledge is power when it comes to hyperglycemia management. Remember there is no hyperglycemia normal range therefore, do regular monitoring of sugar levels. Following a balanced diet, muscle-building exercises, and proper medication are your allies in this journey. Always look out for the signs of hyperglycemia in adults and elderly, and be ready with precautions.
However, it’s not just about managing the physical aspects of hyperglycemia. Emotional well-being and a support system are equally crucial. Reach out to our experienced health experts at Breathe Well-Being for assistance. Together, we can help you choose a healthier, happier life while managing efficiently doing hyperglycemia treatment.
Read More: What Are The Top 10 Early Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes?
FAQs:
What Blood Sugar Level is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is measured through three types of tests. The fasting hyperglycemia range is above 140 mg/dL, and postprandial hyperglycemia is above 180 mg/dL. In the HbA1c test, above 7% is considered the hyperglycemia range.
What is Alcohol Induced Hyperglycemia?
Diabetes patients who drink excessive alcohol experience alcohol induced hyperglycemia. Studies have indicated alcohol causes a rise in blood sugar. So, for diabetics, alcohol consumption is to be limited or best avoided. Unregulated regular consumption of alcohol can lead to hyperglycemia.
How to Treat Non Diabetic Hyperglycemia?
Non diabetic hyperglycemia is a temporary condition and can very well be managed. The doctor may include appropriate medicines along with some lifestyle modifications. These include decreasing carbs intake and increasing fiber and protein-rich foods consumption. Avoiding smoking and alcohol and doing some muscle-building workout sessions daily.
Can Hyperglycemia Cause Headaches?
Yes, hyperglycemia can cause headaches. Although headaches happening due to high sugar levels happen as long-term hyperglycemia symptoms. But with worsening blood sugar conditions, headaches increase in severity. Patients having a record of hyperglycemia are more prone to headaches.
What is the Difference Between Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia?
We can say hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are antonyms of each other. Hypoglycemia simply means ultra-low sugar levels, while hyperglycemia definition says ultra-high sugar levels. In terms of fasting glucose, in hypoglycemia, the blood sugar is below 70 mg/dL. In fasting hyperglycemia, the fasting blood sugar is above 140 mg/dL.
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English