Last updated on September 15th, 2022
Gestational diabetes means high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It affects more than 15% of pregnancies and 1.8 crore births every year. In many women, it is a temporary condition that goes away after birth. However, if the women are at risk of developing gestational diabetes, they should work with the doctor to manage their blood sugar levels throughout pregnancy. They can look for an easy high blood sugar during pregnancy meal plan and exercise regularly to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Maintaining blood sugar levels during pregnancy keeps your pregnancy and baby away from several health-related complications.
Giving birth is one of the most beautiful experiences in the life of a woman. However, this experience can be bitter if a woman has diabetes or develops diabetes during pregnancy. A lot of women with diabetes may have to face severe health complications during and post-delivery. Diabetes during pregnancy affects the mother and also increases the risk for the baby in the womb. Therefore, it is significant to keep the blood sugar levels under control throughout pregnancy to have a healthy pregnancy and healthy babies.

Know About Diabetes During Pregnancy
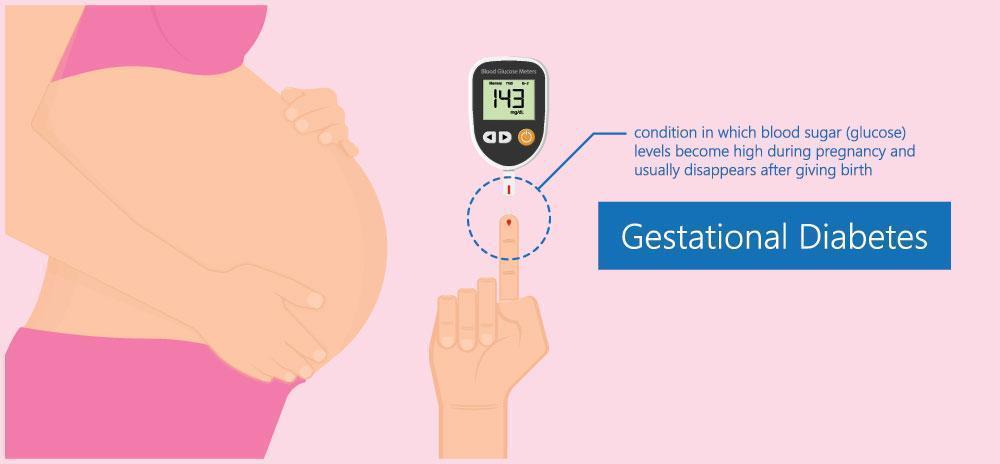
Diabetes during pregnancy is Gestational diabetes. It is a condition in which blood sugar levels become high during pregnancy. It may even affect women who have never been diagnosed with diabetes. There are two types of gestational diabetes: Class A1 and Class A2. Class A1 gestational diabetes is manageable through diet and exercise. However, insulin therapy is needed to manage Class A2 gestational diabetes.

Risk Factors for Developing Gestational Diabetes

Summary
If you are at risk of developing high blood sugar levels during pregnancy, do not delay consulting with your doctor. Timely treatment enables the women to avoid gestational diabetes-related complications during pregnancy.
You are at a high risk of developing gestational diabetes if you:
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are pregnant with more than one child
- Have high blood sugar levels in the previous pregnancy
- Are over 25 years of age
- Have prediabetes before getting pregnant
- Have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or any other health complication related to Insulin
- Had a miscarriage or gave birth to a stillborn baby
- Were overweight or obese before getting pregnant
- Gain more than the usual weight during your pregnancy
- Have high blood pressure before or during pregnancy
Women planning to conceive or are already pregnant should consider the risk factors for gestational diabetes. It will help them to check their blood sugar levels regularly and consult a doctor to avoid developing high sugar levels during pregnancy.
Also Read: Blood glucose levels mmol/l to mg/dl
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
The signs and symptoms of gestational diabetes include:
- Increased, frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Weight loss, even with increased appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yeast infections
These are the common symptoms of diabetes that a woman with high blood sugar levels in pregnancy can also experience. Many pregnant women with gestational diabetes do not face any recognizable symptoms. Thus, they need to monitor their blood sugar levels to check if they have developed gestational diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
Your pancreas releases the hormone insulin. It is a hormone that moves the glucose from your blood to your cells for energy. When you eat something, your body absorbs the carbohydrates and breaks them into glucose. Usually, your pancreas sends out enough insulin hormone to handle the movement of glucose from your blood to your cells. During pregnancy, the placenta makes hormones that cause the glucose to build up in your blood. When the placenta releases more hormones, the insulin hormone in your body cannot handle it well. It leads to a rise in blood sugar levels, and you get gestational diabetes.
Also Read: List of fruits for diabetics to eat
Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes
Summary
According to the U.S. Department of Health, the glucose Challenge test and Oral glucose tolerance Test are the two tests to diagnose gestational diabetes. The healthcare providers recommend gestational diabetes glucose tests to pregnant women who are at risk of high blood sugar during pregnancy. Accordingly, they start treatment for high blood sugar during pregnancy.
Screening of gestational diabetes takes place during routine prenatal care. The screening test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy determines high blood sugar during pregnancy. The screening test varies depending upon the health care provider for determining gestational diabetes. But, the routine screening test for gestational diabetes mainly includes:
- Initial Glucose Challenge Test: It is the first test to diagnose gestational diabetes. It is a type of blood test in which a healthcare provider draws your blood 1 hour after drinking a glucose solution. There is no need to fast for this type of blood test. A blood sugar level of 190 mg/dL or more indicates gestational diabetes. On the Glucose Challenge Test, a blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL or below is considered normal. If the blood test shows high blood sugar during pregnancy, you will need to take an oral glucose tolerance test.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test for diagnosing gestational diabetes is similar to the initial glucose challenge test- except the sweet solution will have more glucose, and the blood sugar test is done every hour for three hours. The glucose tolerance test confirms your high blood sugar during pregnancy. You have high blood sugar during pregnancy if you have at least two of the following values:
Target Blood Sugar Levels for the Pregnant Women
The target blood sugar levels for the women during their pregnancy are:
- Before a meal: 95 mg/dL or less
- An hour after a meal: 140 mg/dL or less
- Two hours after a meal: 120 mg/dL or less
If a woman has a higher or lower value of blood sugar levels than the target levels, she should consult with a doctor. The doctor may suggest suitable medications and lifestyle management tips to maintain gestational diabetes normal range.
Also Read: Diabetes and Skin Problems
Reasons to Treat High Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Summary
In lack of treatment, gestational diabetes poses several risks for the mother and her baby after birth. Therefore, consult your doctor if you are already diagnosed or are at risk of developing high blood sugar during pregnancy.
When a pregnant woman is diagnosed with high blood sugar during pregnancy, she is required to get treatment immediately. Untreated or delayed treatment of gestational diabetes poses risks to both the mother and her baby in the womb. Gestational diabetes increases the risk of:
- Cesarean birth
- Development of diabetes type-2 in mother post-delivery
- High blood pressure during pregnancy
- Hypoglycemia during pregnancy
It also increases the following risks in the babies:
- Premature birth
- Breathing problems
- Type-2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Low blood sugar levels (It can retard the mental growth of the baby.)
Also Read: Dawn Phenomenon and Diabetes
Diet Tips for Women with High Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Summary
The kind of diet you are following during pregnancy affects you and the health of your baby. Thus, pregnant women should take care of their diet during their pregnancy. It helps them to get the best nutrients for themselves and their babies. Along with this, it also enables them to manage their blood sugar levels during gestational diabetes. Your dietician can provide you with diet tips to control your blood sugar levels throughout pregnancy. You can even download the gestational diabetes meal plan app to follow a healthy meal plan.

Glucose is essential for you and your baby during pregnancy. It helps in fetal development and supports your healthy pregnancy. Too much glucose in your body during pregnancy can cause several problems for you and your baby in the womb. Thus, managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy is essential for you and the health of your baby. Here are some diet-related tips to help women with high blood sugar during pregnancy:
Eat more fiber:
Several studies have proven when you eat more fiber, the rate of absorption of glucose in your body gets lower. It also eliminates excessive blood sugar from your body, thereby lowering your blood glucose levels. Try whole-grain bread, brown rice, whole grains, lentils, and beans because they are rich in fiber.
Strictly limit the intake of sugar:
Avoid eating sweets and desserts. They may abruptly increase your blood sugar levels. Cookies, cakes, pastries, and candy often have no nutritional value and contain high calories that can increase your blood sugar levels.
Divide your big meals into smaller ones:
Eating more can increase your blood sugar levels. When you eat more at a time, your body takes more time to digest more carbs from food. It increases your blood sugar levels. Dividing your big meals into three or four meals per day reduces your carb intake at a time. It allows your body to digest the carbs easily and keeps your blood sugar levels under control.
Choose healthier carbohydrates:
All types of carbs affect your blood sugar levels. It is the amount of carbs in your food that makes a difference in your blood sugar levels. However, many studies say choosing complex carbs helps tackle diabetes more efficiently than other types of carbs. Discuss with your dietician about the carb requirements of your body. You can look for the gestational diabetes carb chart to control carb intake. Hence, accordingly, you can choose foods with low carbs. You can choose fruits, vegetables, unsweetened dairy items like yoghurt and milk, lentils, etc. They are the source of healthy carbs.
Control your portion size:
Limit the portion size of your meals to manage your blood sugar levels. It also enables you to avoid weight gain during pregnancy. Remember, body needs are different for everyone. Thus, the portion size for the individual is also different. Talk to your dietician to prepare the best diabetes diet chart to control your portion size.
Choose the food with a low glycemic index:
The glycemic index is an essential factor for people with diabetes to choose their food. It is the measure of how quickly foods containing carbs affect your blood sugar levels. Studies have proven low glycemic foods help reduce postprandial blood sugar. Foods with a high glycemic index quickly affect your blood sugar levels. And foods with a low glycemic index take a longer time. Your dietician can help you choose the food with a low glycemic index to manage your high blood sugar during pregnancy.
Also Read: Triglycerides Levels Chart
Exercise Throughout the Pregnancy
Exercise gives you a lot of health benefits all the time, even when you are pregnant. During pregnancy, exercises help you to stay active and make your body ready for vaginal delivery. Exercising during pregnancy is better for your posture and can avoid common problems like backache and fatigue. Some tips for exercise during pregnancy are:
- Avoid high-intensity workouts.
- Practice yoga and other low-impact exercises that do not put pressure on your belly area.
- Take help from a fitness trainer to practice suitable exercises for pregnancy.
- Walking for at least 30 minutes a day helps in strengthening your pelvic muscles.
Also Read: C reactive protein normal range
Postpartum Care for Women with Gestational Diabetes
Summary
Postpartum care for mothers and their babies is crucial to stay fit and healthy. Women with gestational diabetes or who are at risk of developing diabetes type-2 should take special care to avoid postpartum health complications. They need to know about the symptoms of diabetes, monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, go for a routine check-up, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and breastfeed their babies. It helps them to manage their blood sugar levels post-delivery.
Postpartum care is essential for women with gestational diabetes, even if their diabetes is under control after delivery. Here are a few tips for women with high blood sugar during pregnancy to follow as a part of their postpartum care:
Know the symptoms of diabetes:
Women who never had diabetes but have gestational diabetes during pregnancy are often unaware of the diabetes symptoms. Thus, many women ignore the diabetes symptoms postpartum and ignore the timely treatment. Sometimes, such negligence leads to severe health complications due to diabetes. Therefore, women with gestational diabetes should learn about all the symptoms of diabetes and keep a check on their health.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle:
Women with gestational diabetes should not skip maintaining a healthy lifestyle after delivery. It can cause their blood sugar levels to rise abnormally. They need to continue eating healthy foods and work out regularly. It helps them maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing diabetes type-2. It also prevents them from post-pregnancy gain weight and becoming obese.
Regularly monitor the blood sugar levels:
If a woman has high blood sugar during pregnancy, she should take more care to monitor her blood sugar levels more often. It helps them track their blood sugar levels and lower the risk of developing diabetes type-2.
Start breastfeeding your baby:
Breastfeeding is not only good for babies but mothers as well. If mothers are getting high calories and their blood sugar is rising even after following a healthy diet and daily exercise routine, breastfeeding is good for mothers. It helps in lowering the chances of developing diabetes type-2 and weight gain after pregnancy.
Regular check-ups:
Women with gestational diabetes should not forget that they are likely to be at more risk of developing diabetes type-2. Some of them even get diabetes type-2 after two or three years of delivery. Therefore, they must take all the follow-up medical care. They should visit the doctor for routine check-ups and take their blood sugar tests regularly to monitor their blood sugar levels.
Preventing the High Blood Sugar During Pregnancy
Are you looking for how to prevent gestational diabetes? Adopting healthy habits reduces the chances of developing gestational diabetes. If you have the risks of high blood sugar during pregnancy, eat healthily and get regular exercise. Women planning to get pregnant but are overweight should contact the doctor to manage the weight first before conceiving.
Also Read: Normal blood sugar after eating
FAQ’s
Does lemon water help in managing gestational diabetes?
Lemon water does not directly impact your blood glucose levels. However, it surely helps in preventing the sudden spikes in your blood glucose levels. A glass of lemon water is a simple beverage that you can make and drink. It is low in calories and carbs. Drinking lemon water every keeps you hydrated and, that is essential for people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels under normal.
What is the best treatment for gestational diabetes?
Treatment of gestational diabetes involves eating high-fiber and low- carbohydrate food. The healthy eating habit has to be adjunct with the daily exercise regime to eliminate gestational diabetes. If pregnant women cannot manage their blood sugar levels in the normal range, the doctor may suggest taking the insulin injection. Depending upon the blood sugar levels, the doctor can prescribe either fast-acting insulin injection or long-acting insulin injection.
Do mothers with gestational diabetes experience premature delivery?
Premature delivery is one of the risks due to gestational diabetes. If a mother develops gestational diabetes before 24 weeks of pregnancy, the risk of preterm delivery is higher. However, this risk goes down after the 24th week. Preterm babies can have breathing difficulty, long-term developmental and intellectual disabilities, hearing problems, vision problems, and other health problems. Therefore, pregnant women should keep a check on their blood sugar levels throughout their pregnancy.
Is gestational diabetes treatable during pregnancy?
Many women may never have had diabetes before pregnancy. They develop high blood sugar levels only after getting pregnant. Developing gestational diabetes doesn’t mean that a woman may have to live with it forever. With diet control, exercises, and some medications, pregnant women can get rid of gestational diabetes within two or three weeks. It helps them in reducing the risk of developing complications in their pregnancy.
What range of blood sugar levels is normal for pregnant women?
The blood sugar levels below 140 mg/dL on a glucose tolerance test are normal blood sugar levels for gestational diabetes. Any value of blood sugar levels more than 140 mg/dL but less than 190 mg/dL indicates prediabetes in pregnant women. A blood sugar level of more than 190 mg/dL shows gestational diabetes. If a pregnant woman has blood sugar levels close to 190 mg/dL, she should contact the doctor immediately to avoid complications in her pregnancy due to gestational diabetes.
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English