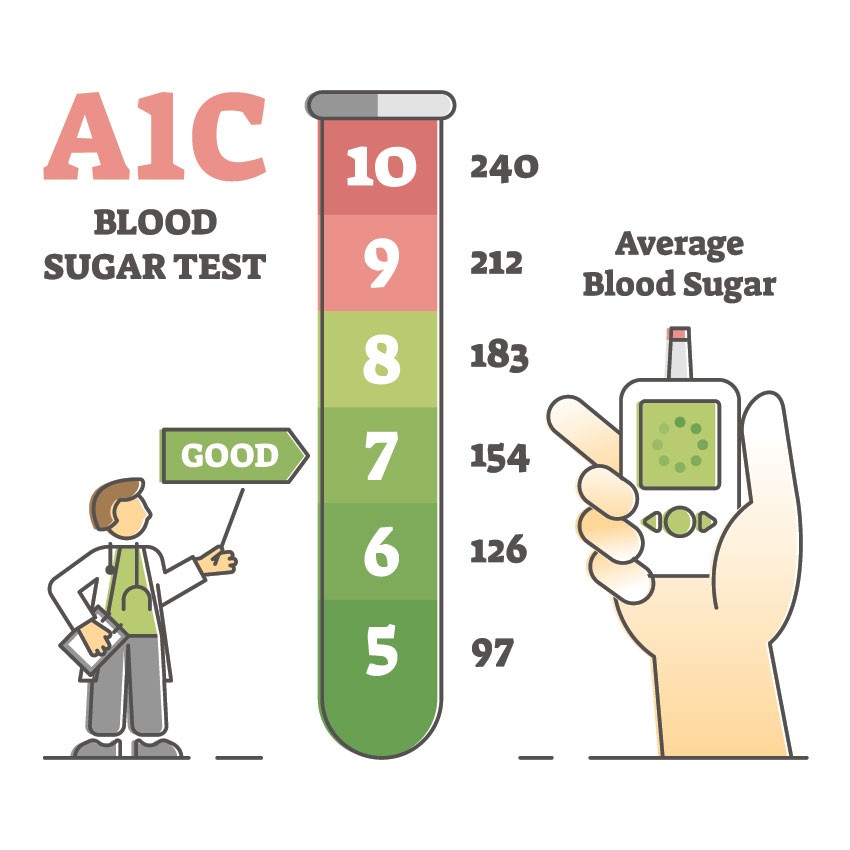
Last updated on September 7th, 2023

What Does mg/dL mean?
There are different units used to measure blood glucose levels, and one such unit is mg/dL.
When the amount of glucose or sugar in the blood is measured in terms of mass concentration, it’s called mg/dL. The mg/dL full form is milligrams per deciliter.
To simply understand mg/dL meaning, imagine a tiny amount (milligrams) of something spread in a small amount of liquid (deciliter).
Mg/dL is used as a blood glucose measuring unit in countries like the USA, Canada, and some parts of Europe.
Read More: Is Type 2 Diabetes Curable/Reversible?

What Does mmol/L Mean?
When we talk about the concentration of glucose or sugar in the blood, using the unit mmol/L, we’re referring to millimoles per liter (mmol/L full form).
mmol/L is used to measure the glucose or sugar in the blood in terms of molar concentration.
Think of a millimole as a tiny group of molecules, and a liter as a big container of liquid. So, mmol/L meaning tells us how many of these tiny groups are in each liter of blood.
Countries that use the metric system, such as many European nations, often prefer mmol/L for measuring blood glucose levels. It’s a different way to express the same idea as mg/dL, which is used in places like the USA, Canada, and other parts of the world.
In this blog, we’ll learn more about the mmol L to mg dL calculator, and vice versa, and various other aspects that you need to know.
Read More: A Guide to Diabetes Mellitus Care Plan
Glycemia or Blood Glucose Definition
Blood sugar levels, known as glycemia, reveal the amount of sugar in your blood. This concentration mostly comes from the food you eat. Among various sugars, glucose is the key player. Though there are other sugars in food, they don’t impact blood sugar like glucose does.
For health analysis, venous blood serum works best. Glucose meters measuring capillary blood might show higher readings after meals due to sugar increase.
Three glycemic states matter:
- Hypoglycemia: In healthy people, it’s under 2.8 mmol/L (50 mg/dL); in diabetics, under 3.9 mmol/L (70 mg/dL).
- Normoglycemia: Normal levels are 2.8 to 5.5 mmol/L (50 to 100 mg/dL) for all; diabetics aim for 3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L (70 to 100 mg/dL).
- Hyperglycemia: Above 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) is hyperglycemia. It’s linked to diabetes, heart/kidney issues. Low sugar, hypoglycemia, leads to tiredness, shaking, and difficulty focusing.
Blood sugar, or glucose, in the blood reflects the energy available to body cells. Insulin, made by the pancreas, regulates glucose levels. In a healthy person, fasting sugar ranges from 72 to 108 mg/dL (4.0 to 6.0 mmol/L). These values are lower in the morning and rise after meals for about 2 hours.
What Are Normal Levels of Blood Sugar?
Normal levels of blood glucose lie between 3.6 and 5.8 mM (mmol/L). In human beings, standard blood sugar levels are roughly 90 mg/dl, which is equal to 5mM (mmol/L). The molecular weight of glucose, C6H12O6, is approximately 180 g/mol, and the total concentration of glucose usually in the bloodstream is about 3.3 to 7 grams (assuming a normal adult blood volume of 5 liters).
Read More: Understanding The Symptoms Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Normal Variations in Sugar Levels: Food & Sugar Levels
Sugar levels in the blood drop to be a sign of hunger. The brain is reliant on sugar as its primary energy source. Low blood sugar triggers the brain that food consumption is required as well as triggers hunger feelings in the person. Sugar gets absorbed from the intestines as well as through the bloodstream, and when it reaches the liver as well as other body cells it delivers energy to the cells.
Sugar levels spike after consumption of food for 60-120 minutes by some grams and are generally found to be lowest in the morning, prior to the initial meal of the day. The levels in the morning are the lowest as it follows about 6 to 8 hours of fasting all over the night.
Read More: Know About PCOS And Its Underlying Symptoms
What Are The Methods by which blood sugar can be measured?
- The international standard means by which sugar levels in the blood can be measured in terms of a molar concentration (mmol/L) (millimoles per liter or millimolar, or mM).
- In the United States, Germany or few other countries, the glucose concentration can be measured in terms of mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Even in India, mg/dL is more commonly used than mmol/L.
Read More: PCOS: Potential Causes, Symptoms, & Treatment Options
Difference Between mmol/L and mg/dL
Both mmol/L and mg/dL are standard units to measure glucose levels in the blood. They provide a measurement of the sugar in the blood, although in faintly diverse ways.
- mmol/L provides the molarity (the number of molecules of any substance within a defined volume, for example, within 1 liter). While mg/dL provides the concentration by the ratio of weight to volume, for example, milligrams per deciliter.
- mmol/L is the common way of measurement utilized in the United Kingdom (blood sugar converter UK), while mg/dL chiefly is utilized in the United States and continental Europe.
Blood sugar characteristically differs from 4 mmol/L to 6 mmol/L for individuals without diabetes. Blood glucose requires strict control in the human body to reduce the risk of complications from developing.
Read More: Connection Between Diabetes and Pancreas
Formula To Convert mg/dL To mmol L and mmol/L to mg/dL:
The following formula can be used for calculation of mg/dL to mmol/L:
mmol/L = mg/dl / 18
The following formula can be used for calculation of mmol/L to mg/dL:
mg/dl = 18 × mmol/L
- mg/dL is milligrams per deciliter
- mmol/L is millimoles per liter
Read More: Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
Here’s a comparison table for difference between mg/dL and mmol/L:
| Aspect | mmol/L | mg/dL |
| Measurement unit | Millimoles per Liter (mmol/L) | Milligrams per Deciliter (mg/dL) |
| Usage | Common in Metric System | Common in US, Canada, Europe, India |
| Normal Range | 3.9 – 5.5 mmol/L | 70 – 99 mg/dL |
| Prediabetic Range | 5.6 – 6.9 mmol/L | 100 – 125 mg/dL |
| Diabetic Range | 7.0 mmol/L and above | 126 mg/dL and above |
| Conversion Formula | mmol/L = mg/dL ÷ 18.018 | mg/dL = mmol/L × 18.018 |
| Preference (Region) | Europe, Most Metric Countries | USA, Canada, Parts of Europe, India |
Read More: Dyslipidemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
mmol/L to mg/dl Blood Sugar Conversion Chart
The blood sugar converter can execute either of the transformations, whether mg/dL or mmol/L. The fasting blood sugar calculator lets an unrestricted amount of conversions and assists in transformation when sugar tests are carried out under special systems.
- mmol/L unit is the molar concentration, also called millimolar (mM), which is equivalent to 18.0182 mg/dL. 1 mmol/L is equal to 18.0182 mg/dL which denotes: Value in mg/dL (mmol/L to mg/dL) = Glucose value in mmol/L x 18.0182
- In the United States, the milligrams per deciliter, mg/dL is more commonly preferred. This is equivalent to 0.0555 mmol/L. 1 mg/dL = 0.055 mmol/L which means: Value in mmol/L (blood sugar mg dl to mmol l) = Glucose value in mg/dL x 0.0555
| mg/dL | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| mmol | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 6.1 | 6.7 |
| mg/dL | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| mmol | 7.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.4 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 11.7 | 12.2 | 12.8 | 13.3 |
Read More: Triglycerides Normal Range, Risk of High Levels, Causes, & Prevention
Blood Glucose Level Chart (Both Measurement Units)
Here’s a more detailed table that covers blood sugar levels, along with their equivalent values in mmol/L and mg/dL:
| Blood Glucose Range | Severity | mg/dL | mmol/L |
| Hypoglycemia | Dangerously low | Below 40 | Below 2.2 |
| Very low | 40-70 | 2.2-3.9 | |
| Normal Range | Healthy | 70-99 | 3.9-5.5 |
| High Blood Sugar | Prediabetic | 100-125 | 5.6-6.9 |
| Diabetic | 126-180 | 7.0-10.0 | |
| High diabetic | 181-250 | 10.1-13.9 | |
| Very high diabetic | 251-500 | 14.0-27.8 | |
| Dangerously high | Above 500 | Above 27.8 |
Read More: List of Drugs That Raise Blood Sugar: Identify Your Medicines Now
Why are Blood Glucose Levels Significant?
Blood sugar measurement and understanding what the sugar levels must be is an important part of diabetes management for lots of diabetics these days. Blood glucose level is nothing but the total amount of sugar circulating in the bloodstream. Various parts of the world have diverse units for measuring blood sugar levels as their standards.
Read More: C-Reactive Protein or CRP Normal Levels Chart For Adults
How to Keep Blood Glucose Normal?

To keep glucose levels in the normal limits:
- Concentrate on fiber (veggies, legumes), complex carbs (brown rice, dark bread), healthy fats (nuts, plant oils, oily fish,), as well as a rich source of protein (lean meat products, legumes, or fish).
- If a person is obese, they must lose the added kilos. Additional pointless fat is associated with diabetes risk, as fat tissue functions as an endocrine organ.
- Quit the habit of smoking.
- Maintain a good and sound sleep; try sleeping at least 7 hours every night.
- Move a lot; try not to sit longer than half an hour at once. Even a one-minute walking break can work for any person.
- Reduce the consumption of alcohol. Opt for dry red wine over beer, sweet wines, as well as colorful drinks.
- Understand how to manage stress levels as stress induces the production of hormones leading to high blood glucose levels.
- If a person has been diagnosed with prediabetes state, consider it a call to action. It’s the final possibility for a person to escape diabetes in the future, and it’s achievable.
Summary
For diabetes treatment to work properly, a person should understand how to manage blood glucose levels. He or she can use a blood glucose calculator to learn about his or her current condition and perform self-management in an improved manner. Understanding blood glucose levels as well as utilizing a blood glucose calculator to track the extent of diabetes is fundamental. A vital part of diabetes management is to be familiar with the glucose concentration levels in the blood and its regulation effectively.
Read More: Keto Flu: Symptoms, Causes & How to Fix it
FAQs
What is a normal mg/dL level?
A normal blood glucose level is typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL before meals. However, this range can slightly vary based on individual factors and medical guidelines. To convert mg/dL to mmol L, use the formula: mmol/L = mg/dl / 18.
Is mmol equal to mg?
No, they’re not equal. mmol measures concentration, while mg measures mass. Both are used for blood glucose measurement but in different ways.
What mmol level is considered high?
A mmol/L reading above 7.0 mmol/L (or about 126 mg/dL) could indicate elevated blood sugar levels.
Where is mmol/L used?
mmol/L is commonly used for blood glucose measurement in countries that follow the metric system, including many European nations.
What is the unit of mmol/L?
The unit is millimoles per liter (mmol/L), used to measure blood glucose concentration.
What is the normal blood glucose for newborns in mg/dL?
mg/dL means milligram per deciliter. Normal blood glucose range for newborns is around 45-100 mg/dL. This range might vary slightly in specific medical contexts.
How to convert mmol/L to mg/dL?
To convert mmol L to mg/dL for blood glucose, multiply the mmol/L value by 18.018. For instance, 5.5 mmol/L equals approximately 99 mg/dL.
Does long fasting spike the levels of blood glucose?
As your body fails to react to insulin similarly, your fasting blood glucose reading may increase, even though you follow a strict diet. The boost in glucose level is your body’s way of ensuring you have a sufficient amount of energy in your systems to awake and begin the day.
Does sugar level enhance with age?
The average blood sugar levels in the fasting state augment with age. This blood sugar rise is significant even when other factors like obesity are kept in mind.
Why is there a spike in my blood sugar levels at 3 am?
In the early morning hours, hormones (growth hormone, cortisol as well as catecholamines) result in the liver discharging huge amounts of glucose into the blood. For a majority of individuals, insulin gets produced by the body to regulate the increase in blood glucose. If the body fails to produce sufficient insulin, blood glucose levels may increase.
What should my blood glucose be when I get up?
To begin the day strong, the ADA suggests that you aspire to get up with sugar levels between 80-130 mg/dL
Can glucose conversion into alcohol occur in the blood?
No, glucose can’t convert to alcohol in your blood. Humans lack the particular enzymes essential for fermenting process of alcohol to occur.
Can the units given by a blood glucose meter be changed?
This all depends upon which glucose meter a person is using. Few meters let you alter the units from mg/dL to mmol/L and vice versa whether few meters are set up only to exhibit one set of blood sugar units. It’s advised to check the meter’s guidebook for whether it is feasible to alter the blood glucose test units. If there is no manual with you, you can discuss it with the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English