Last updated on August 30th, 2022
As the name itself infers, Diabetic Retinopathy is a diabetes-related complication that affects the eyes of the patient. The main cause of this problem is harm to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue present at the retina.
At the initial stage, diabetic retinopathy may not show any symptoms but can cause all sorts of problems ranging from blurry vision to blindness.
People suffering from type 1 or type 2 diabetes can develop this condition. Those who have been suffering from diabetes for a long period of time, or do not have any control on their blood sugar levels are more prone to developing this eye condition.
To keep your eyes safe during diabetes, the best practice one can follow is keeping blood sugar levels in control, and getting a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year.

What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
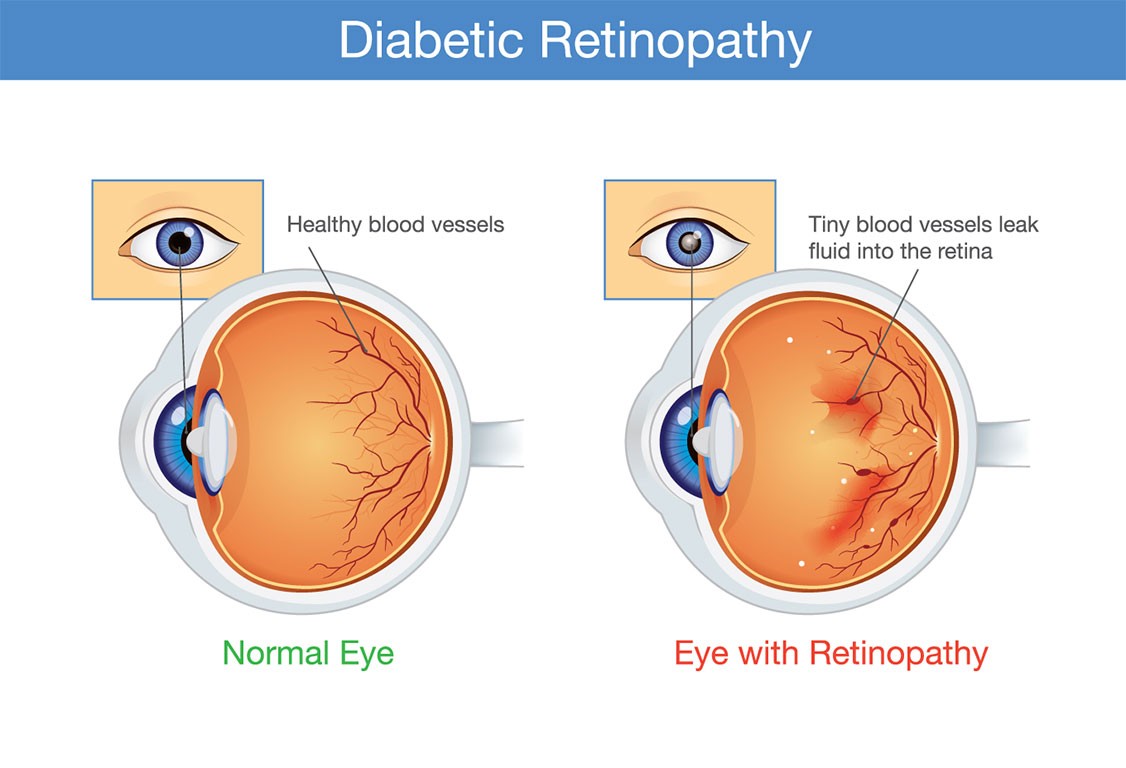
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication caused by Diabetes. It happens because of the presence of too much sugar in the blood that damages blood vessels in the entire body, including in the retina.
The retina is the layer that covers the black portion of your eye. It detects light and then passes on the signal to the brain via the optic nerve.
When the sugar blocks the vessels that carry blood to the retina, it may cause them to leak or bleed. The eyes may start growing new blood vessels which would be weaker and more prone to leakage or bleeding.
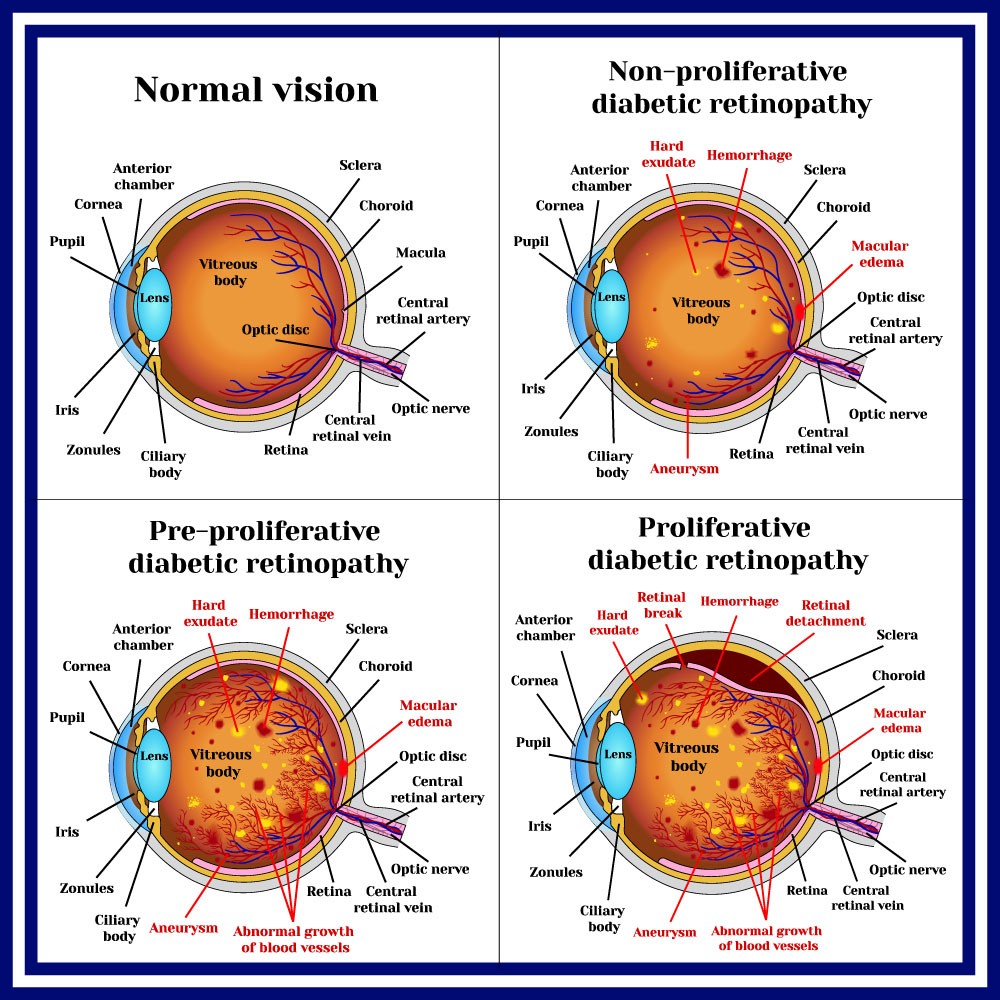
The growth of new vessels in the eyes is known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. This is considered a more advanced stage of the complication. The initial stage of this condition is called nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy.
With constant high blood sugar levels, the eye starts accumulating of fluid, which changes the shape and curve of the eye lens. This process leads to vision impairment.
As soon as the diabetes patient starts keeping the blood sugar levels in check, the fluid accumulation begins decreasing allowing the lens to get back into its normal shape. This starts improving the vision.
Diabetes doesn’t only cause diabetic retinopathy but may also cause other eye conditions like cataracts and open-angle glaucoma.
Also read:- Diabetic retinopathy ayurvedic treatment
Summary
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition caused by diabetes, which may even lead to blindness. It usually occurs because of uncontrolled levels of blood sugar which impacts your retina causing vision impairment.

Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Initially, you may not have any symptoms of diabetic retinopathy. In the later stages, you may experience the symptoms like –
- Black spots floating in the vision (floaters)
- Blurry vision
- Impaired colour vision
- Poor night vision
- Vision loss
- Fluctuating vision
- Empty areas in your vision
Usually, diabetic retinopathy harms both the eyes of the patient.
Also Read: Can diabetics eat watermelon?
When Should You See a Doctor?
To prevent total blindness due to diabetic retinopathy, the patient must keep his/her blood sugar levels in check. If you are a diabetes patient, you must see your eye doctor at least once in a year, if your vision is absolutely fine.
It has been observed that diabetic retinopathy worsens during pregnancy. So, if you are pregnant and also a diabetic patient, you should immediately see your eye doctor, who may suggest some additional tests to keep you safe during the nine months.
You should immediately see your eye doctor if you experience changes in your vision like blurriness, spots or haze.
Causes of Diabetic Retinopathy
As we have already discussed, too much sugar in the blood leads to blockage in the vessels that carry the blood to the retina. Resultantly, the eye tries growing new vessels which do not get strong enough and are prone to leakage.
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
There are two types of this condition –
Early Diabetic Retinopathy
This is a more common type of condition, It is known as nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), in which the eyes aren’t forming new blood vessels.
In this condition, the walls of the blood vessels start weakening, Small bulges start protruding from the walls of small vessels, which sometimes may lead to leakage of fluid or blood in the retina. Secondly, the larger vessels start dilating and getting irregular in diameter. NPDR can keep getting worse as uncontrolled blood sugar levels block more blood vessels.
Even the nerve fibres in the retina start swelling up. At times, the central part of the retina gets swelled up. This condition is called macular edema which requires medical treatment.
Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
When the condition worsens, it is known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. In this condition, the damaged blood vessels get blocked, which leads to growth of new, but weaker, blood vessels in the retina. These veins are very prone to leaking blood into the center of your eyes.
Subsequently, these new blood cells cause scar tissue, which may eventually detach the retina from the back of the patient’s eye. When the new and weak blood vessels affect the flow of fluid out of the eye, it increases the pressure in the eyeball. It can be damaging to the nerve that transmits images from eye to brain, which leads to glaucoma.
Summary
Diabetic retinopathy is of two types – nonproliferative and proliferative. Proliferative is a more severe type of this condition which may result in complete blindness.
Risk factors
Everyone suffering from diabetes is at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. The risk can increase due to the following reasons –
- Suffering from diabetes for a longer duration
- Uncontrolled blood sugar level
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes during pregnancy
- Tobacco consumption while suffering from diabetes
- Being African-American, Hispanic or Native American
Also read:- Diabetologist and endocrinologist difference
Complications
Diabetic retinopathy causes abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina. The complication arising out of this condition can cause serious vision problems that include –
Vitreous haemorrhage
In this condition, the new blood vessels may bleed into the center of your eyes. Depending upon the amount of leakage, you may see a few dark spots, also known as floaters, and may even lose your vision.
Vitreous hemorrhage itself doesn’t cause permanent blindness. The blood stocked inside the center of the eyes usually clears from the eye within a few weeks or in some cases months. If your retina hasn’t sustained any damage, you can regain your earlier vision.
Retinal detachment
The weak blood vessels usually cause growth of scar tissue, which can detach the retina away from the back of the eyes. This may lead to flashes of spots and light in your vision. It can also lead to severe vision loss.
Glaucoma
The weak blood vessels may also grow in the front part of your eyes, which would interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eyes, leading to pressure in the eye. This can eventually cause glaucoma. This pressure can damage the nerve that transmits images from your eye to your brain.
Blindness
Finally, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma or both of these together can lead to complete and permanent blindness.
Also Read: Diabetic Diet Plan
Ways to Prevent Diabetic Retinopathy
The best way to prevent this condition is proper to manage blood sugar levels. Moreover, detecting this problem in the early stage enhances the effectiveness of the treatment.
Following are the ways you can prevent diabetic retinopathy –
- Having a balanced diet
- Do regular exercises
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Stop smoking
- Moderating alcohol consumption
- Keeping blood pressure level in control
- Get regular health screening
Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Mainly, there are three types of processes doctors follow to diagnose diabetic retinopathy –
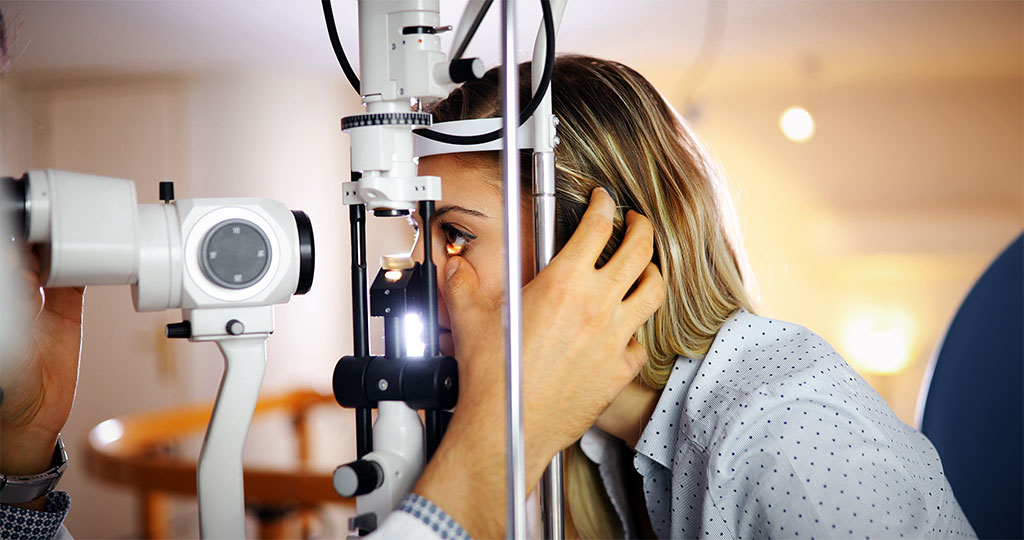
Dilated Eye Exam
This condition is usually diagnosed with a comprehensive dilated eye exam. In this exam, the doctor puts drops in your eyes to widen your pupils, which gives him a better sight inside your eyes. These drops may blur your close vision for a few hours until they wear off.
During this type of eye examination, the doctor looks for the following things –
- Abnormal blood vessels
- Swelling in the retina
- Blood deposits in the retina
- Presence of new blood vessels
- Scar tissue
- Bleeding in the center of the eyes (vitreous)
- Retinal detachment
- Optic nerve abnormalities
Apart from these, the doctor may also check –
- Your vision
- Eye pressure to diagnose glaucoma
- Evidence of cataracts
Fluorescein Angiography
After dilating the eyes, the doctor takes pictures of the inside of the eyes. Subsequently, the doctor injects a special dye into your arm vein and takes more pictures of the eyes to see the dye circulating through the blood vessels of the eyes. Through this method, the doctor figures out which blood vessels are blocked, broken down, or leaking fluid.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT is an imaging test that provides cross-sectional images confirming the thickness of the retina. These images help in figuring out if the fluid has leaked into retinal tissue. This exam can also help in understanding the efficacy of diabetic retinopathy treatment.
Summary
There basically are three different types of eye exams available for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy. A dilated eye exam is the most common of them.
Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy treatment depends upon the severity of your condition and is aimed at slowing down or stopping the worsening of the condition. Discussed below are the ways to treat the condition –
Early Diabetic Retinopathy
In case of having mild to moderate form of this condition, the patient may not require any treatment. The doctor, however, may keep a close watch on your eyes to ascertain the correct timing of undertaking the treatment.
The patients are suggested to keep in touch with their doctor to control their blood sugar levels. When diabetic retinopathy is mild to moderate, it can easily be controlled through proper management of blood sugar levels.
Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
In case of suffering from proliferative form of this condition or macular edema, you may require immediate surgery. The doctor determines the type of treatment depending upon the problem in your retina, which may include –
Photocoagulation
This is a laser treatment, also called focal laser treatment. It can slow down or completely stop the blood or fluid leakage in the patient’s eyes. This procedure fixes the leaks in the abnormal/weak blood vessels through laser burns.
This treatment is usually carried out at a doctor’s clinic in a single sitting. The treatment might not be efficient in terms of restoring your vision completely if you are having blurred vision due to macular edema before surgery, but it has the potential to stop the condition from worsening due to macular edema.
Panretinal Photocoagulation
This is also a laser treatment also called scatter laser treatment. It can shrink the abnormal blood vessels. In this method, the doctor treats the areas or the retina which are not near macula through scattered laser burns. These burns help in shrinking and scarring the weak new blood vessels.
It is also carried out at a doctor’s clinic, generally in two sittings. After the procedure, your vision might stay blurry for a day. You may also lose some of your peripheral or night vision due to the procedure.
Vitrectomy
In this procedure, the doctor makes a tiny incision in your eye to get rid of the leaked blood in the middle of your eye and scar tissue that is placed on the retina.
It is usually carried out at a surgery center or hospital, and the patient is administered general anesthesia.
Injecting Medicine into the Eye
You may also require injections of medication into the center of your eyes. These medications, known as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors, block the effect of growth signals your body sends, which eventually helps in stopping the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
The doctors may also suggest these medications, known as anti-VEGF therapy, as the independent treatment or in combination with panretinal photocoagulation. It is worth mentioning that studies have proven that anti-VEGF therapy has shown great results in treating diabetic retinopathy, but combining it with panretinal photocoagulation is still to produce substantial outcomes.
Summary
There are multiple surgical and laser treatments available to treat or slow down diabetic retinopathy. Notably, surgery usually can only slow down or stop the worsening of this condition and is not a permanent cure.
Takeaway
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that may even make you blind. Hence, keeping in touch with your doctor and maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is really important to keep your vision intact.
As diabetes is a lifelong disease, the patient may experience recurrence of future retinal damage and vision loss. Hence, even if you have undergone treatment for diabetic retinopathy, you must keep getting regular eye exams. Your doctor may suggest you additional treatments in future as per your requirements.
Also read:- food for diabetes patients
FAQs:
What does a person with diabetic retinopathy see?
A patient suffering from diabetic retinopathy may see the following things – spots floating in your sight (floaters), blurred images and fluctuating vision.
How long does it take to go blind from diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy can definitely cause blindness if remained undiagnosed and untreated for a long period of time. It, however, takes severeal years to get to a stage where it could damage your vision permanently.
What causes diabetic retinopathy?
This condition is the result of poorly managed blood sugar levels in the body while suffering from diabetes. Too much sugar damages your retina over time. As retina is responsible for detecting images and transmitting them to your brain through optic nerve, it may cause blindness.
Can diabetic retinopathy go away?
As there is no cure available for diabetes, you can not completely cure diabetic retinopathy. There is always a chance of its recurrence if your health and blood sugar levels are not on the optimal levels.
What are the four stages of diabetic retinopathy?
The four stages of diabetic retinopathy are – mild, moderate, and severe nonproliferative and proliferative.
References:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371617
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/183417#treatment
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English