Last updated on July 28th, 2023
There are more than 10 crore diabetes patients in India in 2023 alone, according to new ICMR data. Individuals might get perplexed between type 1 and type 2 diabetes and often ask about how one is different from another. Even though both forms of diabetes appear similar, there are lots of variations between the two. The difference between both types is in the form of- what causes them, how to manage them, and how they affect the body. In total diabetes cases, diabetes type 1 is known to affect around 10% of people, while type 2 diabetes impacts around 90%. Read this to learn about the major differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, along with a chart.
Many people remain puzzled about both types of diabetes. The person must be aware that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other; in addition, different causes are responsible for their incidence. The major thing to take into consideration is that both are very serious. When a person has high blood sugar levels, serious health complications can occur, regardless of whether it’s type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So, either the condition or the person needs to be very careful and follow the right steps to prevent and manage the condition. Read further to learn details about what causes type one diabetes or type two diabetes and more about the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.

What is Diabetes Mellitus?

Diabetes mellitus is a term for numerous conditions involving the ways by which the body converts food into energy.
When a carbohydrate is eaten, it gets converted to a sugar named glucose by the body, and it is sent to the bloodstream. The pancreas in the body releases a hormone, insulin. This hormone helps in moving the glucose from the blood into the body cells, where the glucose gets used to provide energy to the body.
When any person has diabetes and proper treatment is not given, his or her body doesn’t utilize insulin as it should be used. So, the glucose keeps on accumulating in the blood, a condition generally referred to as high blood sugar. This can create several health problems that might be severe or even critical.
According to top diabetes institutes still, there is no cure has been found for diabetes to date. However, by incorporating certain treatments and lifestyle modifications, a person can live a long and healthy life.
Also Read: Glycomet 500 Uses and Side Effects For Diabetes.

How Common is Diabetes?
Which diabetes is more common? It is found that diabetes type 2 is more common than type 1. Over 1 in 10 people diagnosed with diabetes have type 1, and the rest have type 2. The percentage of diabetics increases with age.
About 10.5% of the general population is suffering from diabetes. Among those, the rate reaches 27% in 65 years and older age groups. Males and females get diabetes at approximately the same rate. Yet, incidence rates are greater among various ethnicities and races.
Blacks and Hispanics have a greater diabetic population than non-Hispanic whites or non-Hispanic Asians. Read on to learn more about the different types of diabetes and its symptoms.
Also Read: Normal blood sugar levels chart
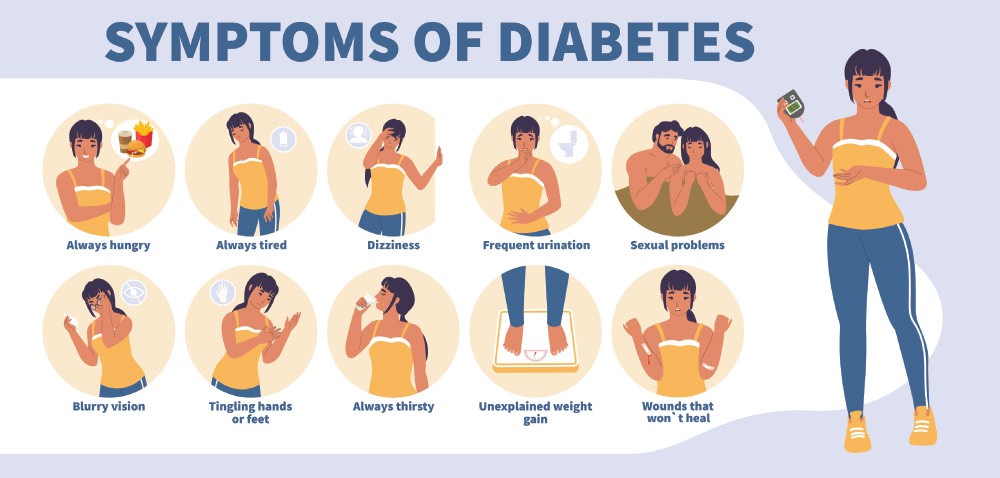
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes vs Type 1 Diabetes
How can you tell if you have type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes? Symptoms of diabetes type 1 and 2 are quite common including:
- Feeling thirsty
- Peeing a lot, especially at night
- Tired feeling more than usual
- Blurred vision
- Weight loss (without trying also)
- Genital itch or thrush
- Poor wound healing
Which is a characteristic of type 1 diabetes mellitus? Type 1 diabetes can often become visible quite quickly. This makes them more difficult to overlook. When the symptoms get ignored, it can cause diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
However, the diabetes mellitus 2 symptoms can be easier to neglect because the condition develops gradually, specifically in the early stages. These reasons make it harder to detect the symptoms. For this reason, it is imperative to know the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Types
Diabetes can be of different types, based on their root cause, these can be
Prediabetes
This condition occurs when the blood glucose is higher than the standard limits but not high enough to diagnose diabetes. More than 15% of Indians are already suffering from prediabetes. Prediabetes makes a person more prone to type 2 diabetes and heart illnesses. More and more exercise and weight management can lower such risks.
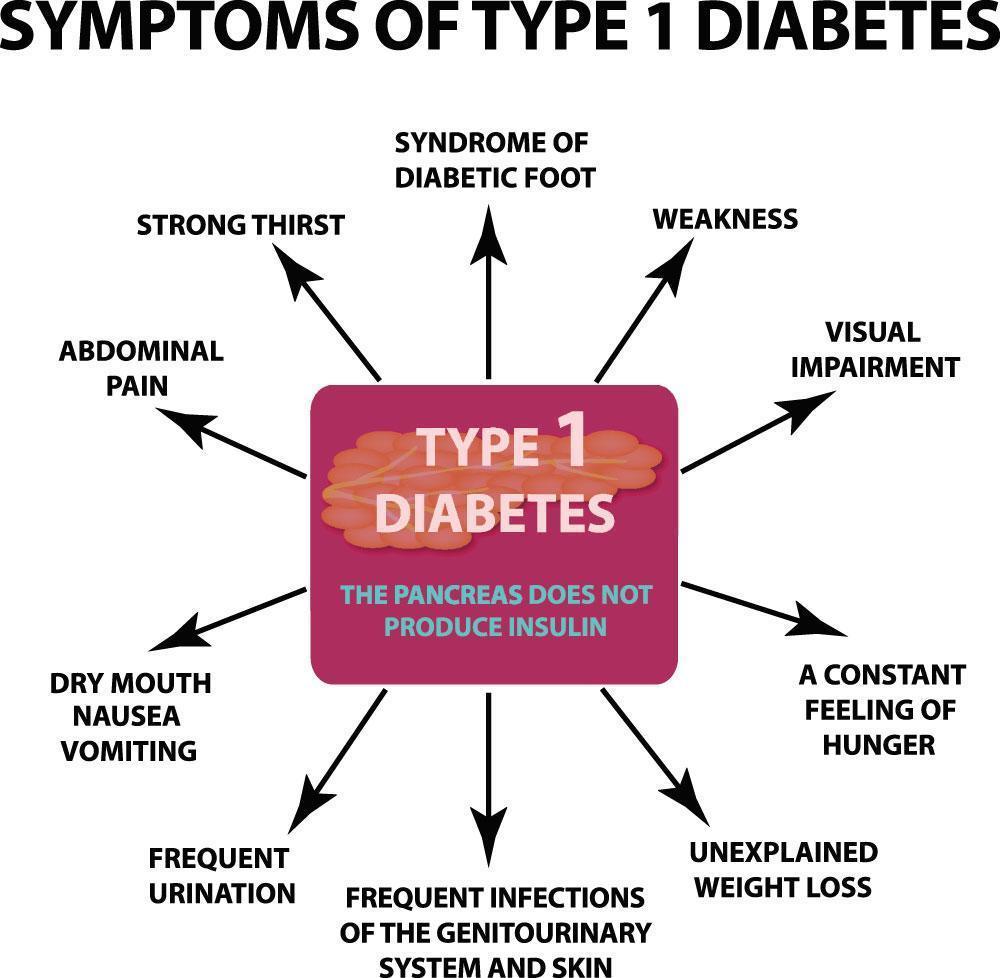
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can also be known as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile-onset diabetes, as this form starts in childhood. It is an autoimmune condition and occurs when a person’s body attacks his or her pancreas with antibodies. It leads to organ damage, and thus, insulin production stops. Type 1 diabetes is a genetic multifactorial disease. This can also occur due to problems in pancreatic cells that make insulin.
Type 1 Diabetes Can Cause:
- Damage to the small blood vessels in the eyes (a condition referred to as diabetic retinopathy)
- Type 1 Diabetes can Damage to the nerves (diabetic neuropathy) as well as,
- Damage to the kidneys (diabetic nephropathy)
- Also, people are at a higher risk of heart disease and stroke.
Treatment for this type involves injections of insulin into the fatty tissue underneath the skin. For this, syringes, insulin pens, jet injectors, or insulin pumps can be used.
If a person is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, then he or she must make changes in their routines, including:
- Careful planning of meals.
- Regular testing of the blood sugar levels.
- Taking insulin or other anti-diabetics as per the requirement.
- Daily exercise and meditation.
Also Read: Metsmall 500 Tablet
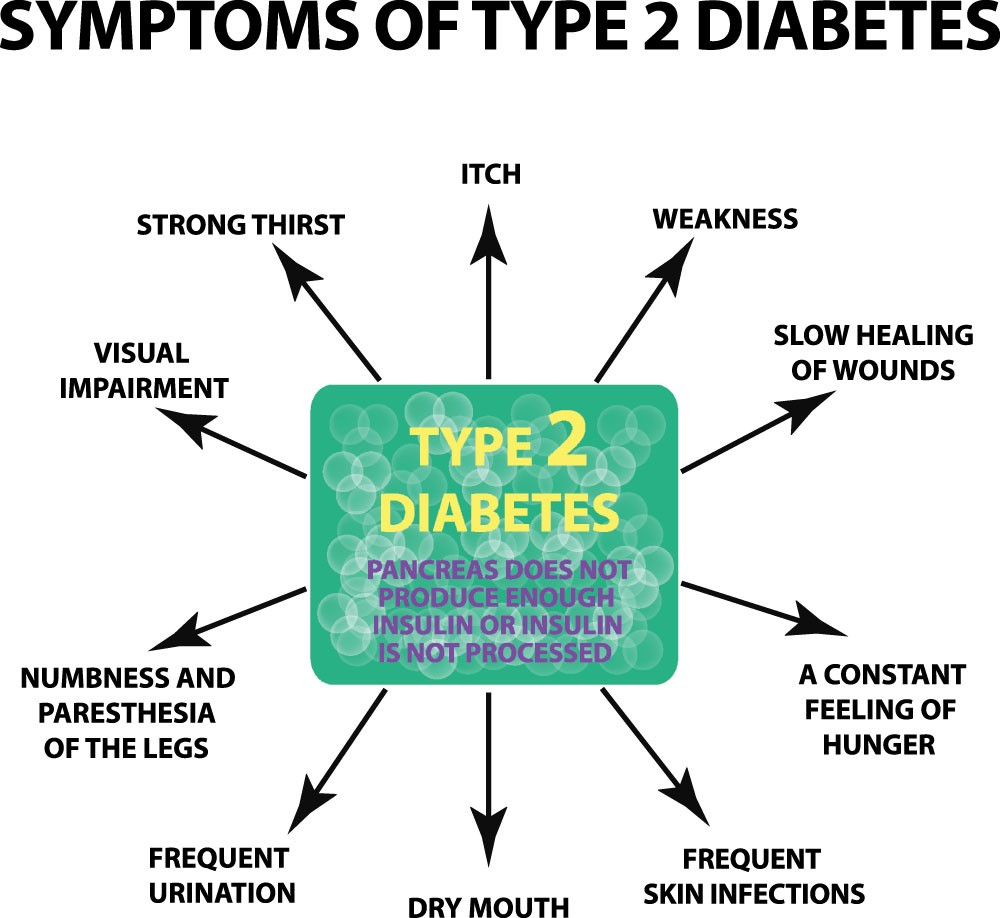
Type 2 Diabetes
Other names of type 2 diabetes are non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset diabetes. It more commonly occurs in children and teens as more young individuals are overweight. Around 90% to 95% of diabetics belong to this type.
In this condition, the pancreas generally produces some insulin, either it’s not sufficient or it’s not utilized by the body as it should. Insulin resistance occurs here, meaning the body cells stop responding to insulin. This condition typically occurs in the liver, fat, and muscle cells.
This type of diabetes is often milder than the first type. Still, it can lead to major health complications, particularly in the small blood vessels of nerves, kidneys, or eyes. This type also increases the risk of heart ailments.
Treatment involves eating a balanced portion of the meal, keeping a healthy weight, and exercising. Also, sometimes anti-diabetic medicines are prescribed.
Also Read: Biguanides: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Interactions & Precautions
Gestational Diabetes

Pregnancy generally leads to some sort of insulin resistance. If this resistance shapes into diabetes, it’s named gestational. It is usually spotted in the middle or late pregnancy. As a female’s blood glucose passes through her placenta to the baby, it’s mandatory to control gestational diabetes to protect the baby’s growth and development.
Physicians report this type in around 2% to 10% of pregnancies. It generally fades away after birth. But up to 10% of females with gestational diabetes get type 2 weeks or even years afterwards.
This type of diabetes is more of a risk for the baby as compared to the mother. An unusual weight gain can be seen in the baby before birth, or there can be breathing difficulty in the baby at birth, or later on, the mother can be at a greater risk of obesity and diabetes. The mother may require a cesarean section due to an exceedingly large baby.
The treatment involves:
- Careful meal planning to obtain maximum nutrients without fats or calories.
- Keeping weight gain under control.
- Daily exercise.
- Taking insulin to control the raised sugar levels (only as per the need).
Managing and Treating Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Managing and treating your diabetes is so important. This is because it’ll help you avoid serious health complications. And it’ll play a big part in your daily life regardless of if you have type 1 or type 2.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin to control your blood sugar levels. You’ll also need to test your blood glucose levels regularly. And count how many carbs (carbohydrates) you eat and drink. Counting carbs will help you work out how much insulin you should take when you inject it into your meals.
And generally, you should be trying to have a healthy lifestyle. That includes regular physical activity and a healthy, balanced diet. These will help you reduce your risk of diabetes complications.
If you have type 2 diabetes, you also need to eat a healthy diet and be active. These things will help you manage your weight and diabetes.
Summary
Type 1 and type 2 are dissimilar in their root causes, but their effects are ultimately similar. Below is a table depicting some of the major differences between type 1 and type 2.
Also Read: Galvus Met 50/500 MG Tablet Uses, Side Effects, Dosage & Interactions
Difference Between Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Chart
| Type 1 | Type 2 | |
| What occurs in this type? | A person’s body attacks the beta cells (present in the pancreas), indicating an inability to make insulin. | The body is incapable of making adequate insulin, or the insulin produced fails to work suitably. |
| Symptoms | The type 1 signs appear more rapidly. | Diabetes mellitus 2 symptoms can be easily missed as they appear gradually. |
| Risk factors | Causes remain unknown.
People up to 40 years are more expected to be diagnosed with it, particularly children. Most children experiencing diabetes have type 1. |
A few things that can put a person at risk of type 2 diabetes may be weight, age, or ethnicity. |
| Management | By taking insulin to control the levels of glucose in the blood. | Through medication, physical activity, and consuming a balanced diet. However, people here also may be prescribed insulin. |
| Cure and Prevention | Currently, no cure is available for type 1, but research is going on. | It cannot be cured, it can only be prevented and put into remission. |
The Emotional Impact of Both the Diabetes Types
Diabetics can sometimes feel devastating.
Both type 1 and type 2 are different from each other, but feeling disturbed or anxious on account of diabetes can influence any person. It is significant to note that this chronic condition can be associated with an emotional, psychological, and mental impact regardless of the cause or treatment behind it.
If you’re fighting your diabetes, keep in mind that you’re not alone. Loads of helplines are available to you, just like ours: BREATHE WELL-BEING. Contact us and discuss your problems with our expert health coaches and nutritionists.
Breathe Well-being Diabetes Reversal Program is a holistic patient care program designed to inspire diabetics to introduce a few healthy lifestyle changes and stick to them. At Breathe Well-being, Type 2 Diabetes patients are engaged so that their condition can be managed or reversed to live a healthier life free from diseases. The company’s proficient health coaches help the user evade negative emotions from past failures in losing weight. And they help to boost their motivation. With the help of this program, user has the ability to make better decisions in getting rid of their Diabetic medications.
Here at BWB platform, you can also read about other people’s experiences that are going through similar phases via our forum. Mind it, a lot of things can help you deal with the problem. It’s just about searching for what works for you!
Also Read: Triglycerides Levels Chart: Normal, Risk of High Levels, Causes, & Prevention
FAQs:
Why do people with diabetes type 2 gain weight?
Consumption of lots of calories than the body requires will bring about increased sugar levels. If the cells fail to eliminate glucose from the blood, the body will store it in the tissues as fat. When an individual takes insulin as a diabetic therapy, their body may absorb too much glucose from food, resulting in weight gain.
Can walking reverse diabetes?
Studies have found that walking can be useful in reducing blood sugar and thereby controlling diabetes.
Can I reverse diabetes type 1?
The truth is, while the management of diabetes type 1 with diet, insulin, and exercise, at present no treatment.
Can you have both types of diabetes?
Double diabetes is the condition when a person with type 1 diabetes develops insulin resistance (which occurs in type 2 diabetes mellitus). Any person with double diabetes will always have diabetes type 1 but the insulin resistance effects can be lowered to some extent.
Which condition is poorer, type 1 or 2 diabetes?
Type 2 is much milder than type 1. However, it may result in major health complications.
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English