Last updated on September 14th, 2023
Type 2 diabetes is becoming a raging concern in India. India stands on second place in the number of diabetic patients in India, just behind China. This epidemic is the outcome of an unwatched lifestyle that is causing this spread amongst youth. Type 2 diabetes is the result of insulin resistance that resists the body to process the glucose levels in the body. Let’s read about Insulin resistance and its symptoms, causes, tests, treatments and preventions in this blog.

What is Insulin Resistance?
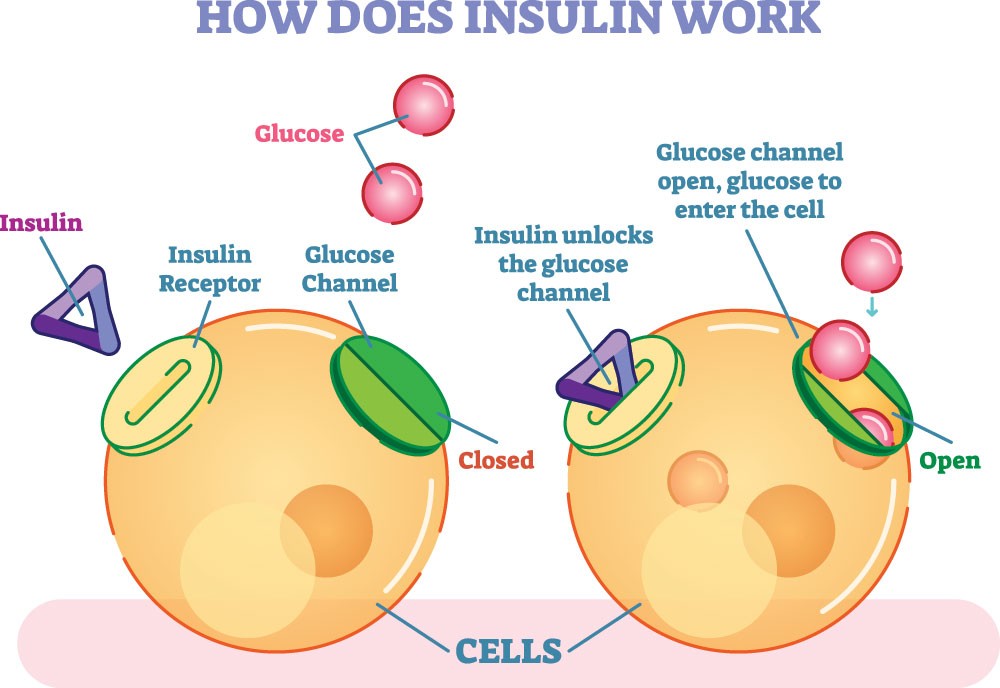
It is the resistance of the body towards the Insulin Hormone that acts to control sugar levels in the body.
Insulin is a hormone that regulates the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells do not respond normally to insulin. Because glucose cannot enter cells as easily, it accumulates in the blood. This can progress to type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance is usually asymptomatic. Exercise and weight loss can help reverse insulin resistance.
Also Read: Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart

Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance does not alarm quickly although one can identify its beginning with a few symptoms. It can cause a variety of physiological changes. These insulin resistance symptoms can be tested through some readings and others through fair vigilance.
Diagnostic Symptoms that can be identified through physiological tests:
- High Blood Pressure (>130/80)
- Overweight (waist size >35-40)
- High Blood Sugar Levels (Fasting: >100 mg/dL)
- High Triglycerides Level (Fasting: >150 mg/dL)
- Low HDL (Good Cholesterol) Level (<40 mg/dL in men, <50 mg/dL in women)
Apart from these diagnostic symptoms, other symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and appetite
- Dark patches on the skin called acanthosis nigricans (neck, armpit, groin)
- Frequent urination
- Constant hunger
- Tingling in hands and feet
- Fatigue & tiredness
Sometimes doctors suggest running some tests to diagnose type 2 diabetes in case of fewer symptoms.
Read More: Can Diabetics Eat Jaggery?
Risk Factors and Causes of Insulin Resistance
Type 2 diabetes is a lifestyle-borne disorder that is affecting millions of people across the world. The sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy food are triggering insulin resistance even more. It generally starts at the age of 40 but nowadays it is seen in the young population too. Physical inactivity and junk food are major reasons for these upscaling numbers. If there are some visible symptoms, a doctor can suggest going for tests to diagnose type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. The risk factors and causes of insulin resistance involve:
- Increased weight, obesity, or excess fat around the belly
- Inactive or sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of diabetes
- High carb diet
- Low HDL (good cholesterol) level
- High triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Unhealthy food
- Disturbed routine for food and exercise
- Gestational diabetes
- Condition of prediabetes
- History of stroke
- Ethnicity or age
- Sleep problems like sleep apnea
- Certain medications like steroids or antipsychotic
- Mothers who delivered a baby over 9 pounds of weight
- Pancreatitis
- Liver conditions
Above mentioned are certain risk factors and causes of insulin resistance that lead to type 2 diabetes and spike blood sugar levels. If someone is suffering one or other symptoms of insulin resistance and falls into the bracket of those risk factors, a doctor can suggest running some tests.
Also Read: C-Reactive Protein or CRP Normal Levels Chart For Adults
Diagnosis and Tests for Insulin Resistance
To diagnose the diabetic condition, a doctor asks certain questions following some tests. After analyzing the symptoms and risk factors of insulin resistance, a doctor can conclude whether the tests are required or not. To carry out this process, a doctor needs to confirm certain conditions to diagnose and test for insulin resistance:
- Family history of diabetes
- Physical tests like weight and blood pressure
- The final step to diagnose insulin resistance is to run some tests
The following are the test for insulin resistance:
Fasting blood glucose test
This is a blood test which is carried out after fasting for a minimum 8 hours. This test shows the reading of blood glucose levels without eating anything. Based on the readings, it will measure your insulin resistance whether one is diabetic or not.
- If the fasting blood sugar measures under 100 md/dL, it is considered a normal range.
- If the fasting glucose level is between 100-125 mg/dL then it points to prediabetes.
- If the levels exceed 126 mg/dL then this is diagnosed as insulin resistance or in other words diabetes.
Glucose tolerance test
This is a slightly more advanced test that confirms insulin resistance. Following a fasting glucose level test, a sugary drink will be administered. After 2 hours, the sugar levels are checked to diagnose insulin resistance in the body.
- Normal: If after drinking a high-sugar drink, one’s sugar levels after two hours is less than 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: If sugar levels fall in the range between 140-199 mg/dL then this condition is called prediabetes
- Diabetes: If the blood glucose level is above 200 mg/dL then it confirms the presence of insulin resistance or diabetes.
Hemoglobin A1C test (HbA1C Test)
This blood test determines your average blood sugar level over the previous two to three months. It is used by doctors to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. If you have diabetes, it can help you determine whether it is under control. You may need to retake the test to confirm the results.
Random blood glucose test
When experiencing some symptoms, one can get the sugar tested through a random blood glucose test. Although it does not determine the actual diabetic condition or insulin resistance so to diagnose insulin resistance, above mentioned three tests are more agreeable and suggested by doctors.
Read More: Natural Remedies to Control your Diabetes at Home
Insulin Resistance Treatment and Prevention
Insulin resistance is not an irreversible condition. One can prevent insulin resistance from progressing into type 2 diabetes by following certain protocols. Insulin resistance treatment and prevention include a few lifestyle modifications that can reverse the type 2 diabetes condition. It helps to maintain a healthy blood sugar level. Insulin resistance treatment and prevention include:
Physical Activity
The best way to reduce insulin resistance and increase insulin sensitivity is to exercise. An active routine may include brisk walking or a few exercises. 30 minutes of daily workouts can bring significant improvement in insulin resistance.
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet includes low-carb, low-calorie, low-fat, high-fiber, and rich-nutrient foods. It helps to control blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy BGL. Avoid high-carb and junk food that spikes glucose levels and also increases weight.
Weight management
A healthy weight helps to lead a healthy life. If you are overweight or have belly fat then try to reduce weight through exercises and diet to prevent insulin resistance. You don’t need to go crash dieting or to shed many pounds, just reducing 7% of your weight can bring significant health benefits to reduce insulin resistance.
Medication
In case of high blood glucose levels, a doctor can suggest some medications like metformin. It can help to prevent and treat insulin resistance.
These are the few ways that increase insulin sensitivity and help to control rising blood glucose levels, eventually controlling type 2 diabetes.
Also Read: Indian Diet Chart for Diabetics
Complications of Insulin Resistance
If insulin resistance remains untreated, it leads to various health complications. Insulin resistance is the condition where the body does not use the insulin hormone in an effective way that increases the glucose levels in the blood. An increased glucose level accelerates the complications of insulin resistance and can affect various organs. Complications of insulin resistance include:
High Blood Sugar Levels (Hyperglycemia)
Untreated insulin resistance progresses into high blood glucose levels that worsen the diabetic condition and affect overall health.
Low Blood Sugar Levels (Hypoglycemia)
Insulin resistance also triggers the condition of low blood glucose levels, which is a fatal situation, if not treated on time.
Heart Attack or Cardiovascular Disease
High glucose levels in the blood lead to high cholesterol levels. This narrows down the width of arteries or blood vessels. This condition is called atherosclerosis. It causes poor blood circulation which leads to heart attack and other cardiovascular conditions. Insulin resistance is very likely to set off heart problems.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver condition (NAFLD)
Increased glucose levels in the blood impact liver function and cause various liver conditions. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is one of those conditions caused by insulin resistance. Fat accumulation in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol is known as NAFLD. This can be prevented with the treatment and prevention of insulin resistance.
Type 2 Diabetes
This is an outcome of increased insulin resistance if not being taken care of on time. Insulin resistance leads to type 2 diabetes which is an incurable condition and brings various chronic health problems.
Kidney Diseases
It also affects kidney functions by impacting metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance elevates the risk of chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Eye Problems
Insulin resistance causes fluctuating blood glucose levels that affect eye health significantly. It affects the vision and lens. People with high insulin resistance or diabetes face various eye problems like blurry vision, glaucoma, cataract, or even retinopathy. So it’s important to increase insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels.
Increased Prothrombotic State
Insulin resistance escalates the prothrombotic factors that lead to venous thromboembolism. This is the condition where blood clots form in the veins and affect the smooth blood flow.
Cancer
Insulin resistance causes the formation of unbreakable fat cells. This leads to increased weight, inflammation, and various hormonal imbalances. Thus, insulin resistance can cause various types of cancers.
Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Insulin resistance and brain conditions are closely related. Disrupted insulin functioning in peripheral tissues accelerates the situation. Also, insulin resistance impacts brain insulin receptors and leads to neurotransmitting conditions. It affects the proper functioning of the brain and impairs memory. Then, it leads to severe conditions like Alzheimer’s and dementia.
FAQ’s:
How do I know if I am insulin resistant?
Insulin resistance is a condition where the body stops responding to the insulin hormone. It increases blood sugar levels in the body. Symptoms of insulin resistance are overweight, high BP, high sugar levels, high triglycerides, increased thirst and appetite, frequent urination, fatigue, tiredness, dark patches on the skin called acanthosis nigricans (neck, armpit, groin), tingling hands and feet, etc.
What is the difference between insulin resistance and diabetes?
Not all insulin-resistant people have diabetes. Insulin resistance happens when your body’s cells do not respond well to insulin. Insulin is the hormone that transports glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used for energy. It takes more insulin to complete this process when you have insulin resistance. The pancreas secretes more insulin to compensate for insulin resistance. This aids in the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Whereas in diabetes, the pancreas does not produce insulin at all or produces not enough. Also, in prediabetic and diabetic conditions, the body is unable to use produced insulin. Insulin resistance is affected by various factors like food, exercise, sleep, stress, and medications.
How Insulin Resistance Progresses to Type 2 Diabetes?
Insulin hormone helps to manage blood glucose levels in the body. In the case of insulin resistance, the pancreas releases more insulin to control rising sugar levels in the body. But if insulin resistance is not prevented or treated, it affects the pancreas for a long time. This will progress to prediabetes and then type 2 diabetes. To prevent developing type 2 diabetes from insulin resistance, one should follow a healthy diet and exercise regime.
How common is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a prevailing condition in the 15.5-46.5% adult population globally. This is the consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle and obesity. This is an alarming situation as more and more population is being affected by it. Although, this condition can be improved by the inclusion of a healthy diet and exercises in your daily life.
Who does insulin resistance affect?
Insulin resistance affects people who are suffering from obesity, have a family history of diabetes or insulin resistance, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy eating habits, gestational diabetes, have a smoking habit, have conditions like PCOD or NAFLD, etc. They are more likely to be impacted by insulin resistance.
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English