Last updated on September 27th, 2022
Insulin is an essential hormone for metabolism in the human body. Its primary purpose is to move grape sugar (glucose) from the blood into the cells. There the sugar molecules are needed to generate energy. Read this blog to know about types of insulin with the help of chart.

Insulin: Formation
Summary
Insulin is produced in the pancreas, more precisely in the beta cells located in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. Hence the name: Insulin comes from the Latin “insula,” in English, “island.” The beta cells first produce a precursor, proinsulin. It splits up into an insulin molecule and a so-called C-peptide. Both are distributed in the same proportion. You can measure the level of the C-peptide in the blood – and in this way, you can determine whether the body is still producing its insulin.
The body also produces the hormone glucagon in the alpha cells of the pancreas. It is the antagonist of insulin: while common insulin lowers blood sugar, glucagon promotes the formation and release of the sugar reserves mainly stored in the liver into the blood and causes the blood sugar level to rise.

Working of Insulin in Human Body
Summary
The small intestine breaks down carbs from food into glucose. These sugar molecules then pass through the intestinal wall into the blood. From here, they distribute to the various body cells. There, they generate energy.
Insulin is the key that opens the cells to the sugar molecules. Insulin docks to the insulin receptors on the cell surface. In this way, the glucose can get into the cell interior from the blood vessels. Disturbance in this mechanism occurs in type 2 diabetes. Here, the sugar remains in the blood. Hence, the blood sugar level rises.
Also Read: How to Reduce Blood Sugar Level Immediately?
Insulin transports sugar into the cells of:
- muscles
- liver
- kidneys
- fatty tissue
- but not into the brain
The brain cells can absorb glucose independently of insulin. The body also stores glucose, which it does not immediately need for energy production, in glycogen in the liver and especially in the muscles.
In addition to this crucial function, insulin has other parts in the body. This is how it affects the appetite sensation in the brain. The hormone also inhibits the breakdown of fatty tissue ( lipolysis ). When there is a complete lack of insulin, the body draws on the adipose tissue for energy production when no sugar gets into the cells. The result: Free fatty acids flood the organism, leading to ketoacidosis or over-acidification of the blood. This severe metabolic imbalance can mainly occur in type 1 diabetes, less often in long-term type 2 diabetes.
The structure of human insulin is similar to that of human insulin. Analog insulins, on the other hand, have a different structure. They, therefore, work remarkably quickly and briefly or mainly slowly and long-lasting compared to regular insulin. There are many types of insulin that will be discussed below.
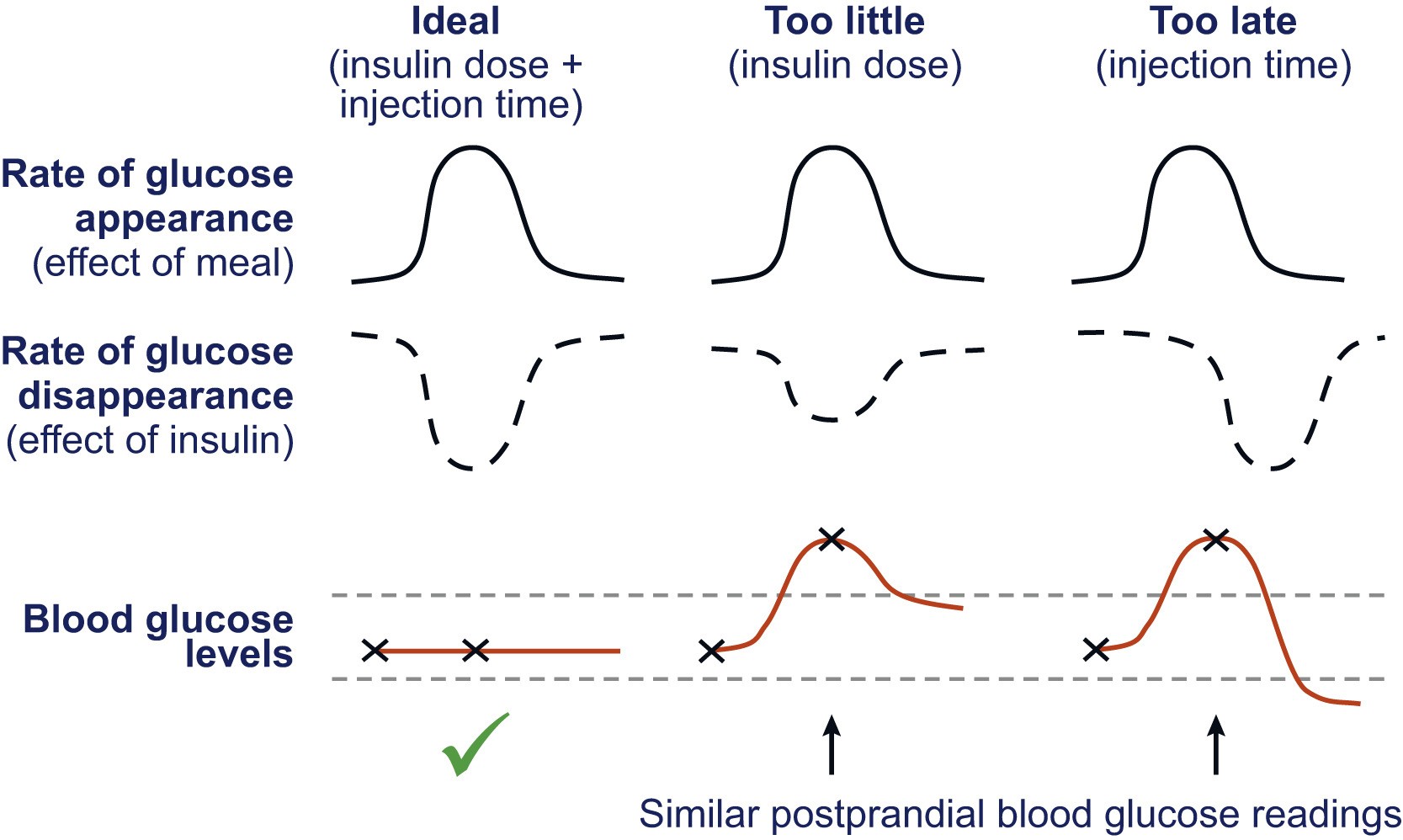
Important: The following information on the onset, maximum, and duration of the effect are rough guidelines. The actual impact of insulin preparation can vary significantly from person to person.
Also Read: Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart By Age
Fast-acting Insulin
Summary
In diabetes therapy, they serve to cover the insulin requirement with meals, the so-called bolus. In addition, blood sugar levels that are too high for a short time can be corrected with a dose of fast-acting insulin.
Compared to human insulin, fast insulins like humulin r 500 have the advantage that they make it easier to intercept increases in blood sugar after eating and that hypoglycemia due to prolonged action can be better avoided.
The blood sugar lowering effect usually occurs after around ten to 15 minutes and with particularly fast turbo insulin even after five minutes. The most significant impact is often reached after approximately an hour before it subsides after around three hours. With human insulin, the peak is reached after two to three hours. The effects can last up to eight hours.
Also Read: How to Reverse Diabetes Permanently?
Fast-acting Insulin Working
Depending on the insulin preparation and the current blood sugar level, injecting fast insulin a specific time before eating can be helpful. The planned meal should prevent the values from rising too much before the insulin effects. When it makes sense to keep a spray-eating interval and how long it should be, people with diabetes always clarify with their doctor as part of the therapy setting. Thanks to modern turbo insulins, it is often unnecessary to eat or drink between meals these days.
Insulin for cartridges and pumps is usually available in a concentration of U100. U100 means that one milliliter of liquid contains 100 units of insulin.
Long-term and short-term insulins are also occasionally available. These come in pre-filled pens in the concentrations U200 and U300. Higher concentration:
- Extends the duration of action
- Reduces the volume of the injection.
Long-acting Insulins
Summary
They cover the body’s basic need for insulin, independent of meals. Long-acting insulins are also called basal insulins. They are usually injected one or two in a day. Long-acting insulins are designed to mimic the biological activity of the pancreas regardless of what you eat. This continuously releases small amounts of insulin into the blood to keep the sugar levels stable.
There are also various preparations for long-term insulins that differ in their behavior. The effect occurs after an hour or later and ends after around 16 to 24 or even 48 hours. Since long-term insulins have a flat curve of action, they do not have as pronounced a maximum effect as other types of insulin.
Delay insulins strike a middle ground between short-acting and long-acting insulins. They are also called intermediate insulins, nph regular insulin (neutral protamine hawthorn) is human insulin, which is delayed due to the addition of protamine. It has a more pronounced peak of action than actual long-term insulin. The risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia is greater with delay-release insulin than with long-term insulins.
Mixed Insulins
Summary
Mixed insulins contain one short-acting and one long-acting insulin. They are available in different combinations (human insulin + NPH insulin; short-acting analog insulin + delay substance) and in different mixing ratios (for example 30/70 = 30 percent fast-acting + 70 percent long-acting insulin).
The proportion of short-acting insulin is between 15 and 50 percent, depending on the preparation. Mixed insulins like nph 70 30 are used as a part of conventional therapy (CT). They are particularly suitable for people having a regular daily routine. This routine involves fixed eating and exercise habits.
Also Read: Glipizide side effects
Charts of Types of Insulin
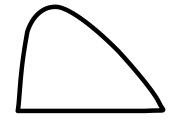
Activity profile of human insulin / regular insulin:
Fast insulin analogs
In a solution, the insulin molecules stack together. They form what are known as hexamers. Hexamers is a group of six insulin molecules. These are dimers if there are two. One can also exchange individual amino acids in regular insulin. A person can thus, achieve that these hexamers disintegrate more quickly. That too, in the subcutaneous adipose tissue after the injection. In insulin glulisine, replacement of amino acid asparagine (in place B3) is done with lysine and lysine (in place B 29) with glutamic acid. In the case of insulin aspart. It was possible to achieve faster monomer formation. This can be done by replacing the amino acid proline with aspartic acid instead of B 28. A quicker absorption into the bloodstream of the insulin molecules is also possible. This can be achieved via additives in the insulin formulation:
- EDTA / citric acid
- magnesium
- organic chaperones
- niacinamide.
Add niacinamide (vitamin B 3) to insulin aspart. This leads to faster absorption (faster aspart). Rapid insulin analogs control the postprandial sugar peaks. The duration of action is shorter than regular insulins. Thus, no snack is necessary.
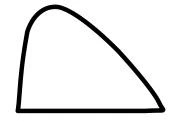
Action profile of fast analog insulin: You can better adapt the insulin levels to the natural insulin secretion with short insulin analogs.
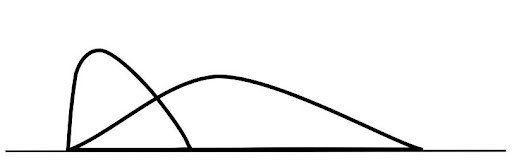
Basal insulins (delay insulins)
If you add zinc and neutral protein hawthorn (NPH insulin) to the liquid, the duration of action is longer. These insulins are cloudy because it is not a solution but a suspension. Therefore, you must swirl them (not shaken) at least 20 times to ensure that the insulin molecules are evenly distributed.
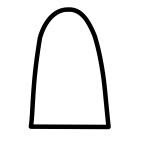
Effect profile of an NPH delay insulin:
Long-term analog insulins
Exchange the individual amino acids. Doing so, sticking of the individual insulin molecules is possible in the subcutaneous fat tissue for a long time. Then, break down into individual insulin molecules after a delay. Then, it can absorb into the bloodstream.
The first analog insulin with an extended duration of action was insulin glargine. After the patent expired, similar insulins, so-called “biosimilars,” came onto the market from other companies. A longer duration of action is also possible. By attaching a fatty acid chain (Levemir / Degludec). These insulins bind to albumin in the blood. Their release occurs slowly back to the receptor by the albumin.
Also Read: how to check blood sugar
Effect Profile of Long-term Analog Insulin:
High Concentration of Insulins
Obesity continues to increase. Hence, higher and higher doses of insulin are necessary to normalize blood sugar. This creates a problem with the amount of fluid injected into a site. The insulins like humulin r u 100 all had a concentration of 100 IU / ml until recently.
Typically, no more than 40 units must be applied. That too, subcutaneously to any one site. If higher doses were necessary, the patient had to inject twice. The insulin manufacturers have therefore developed insulins with a higher concentration.
Mixed Insulins
NPH insulins and long-acting insulin analogues are used in BOT (Basal Supported Oral Therapy). Individually defined HbA1c is not achieved with tablets or GLP-1 receptor agonists. Then, a BOT is done in the next step.
Administration of regular or fast-acting insulin analogues occurs with meals. Then, basal insulin with essential bolus therapy or ICT is given.
For selected, especially older patients, mixed insulins simplify therapy. Mixed insulins are a ready-made mixture of:
- human insulin
- a fast-acting insulin analogue
- basal insulin.
The application occurs before breakfast and before dinner. Due to the basal insulin content in the mixture, there is also an insulin effect around lunchtime. And, thus the insulin needs of a smaller meal are covered.
Effect Profile of a Mixed Insulin
Also Read: how to breathe to lower blood pressure
FAQs:
What is premixed insulin type?
A mix of regular and Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin is known as premixed insulin. Some of the common types of premixed insulin are Humulin M2, M3 and M5.
Which are the most common soluble insulin brands?
Soluble insulin is the short-acting type of insulin. It is also known as neutral and regular insulin. Some of the common soluble insulin brands are Humulin S, Velosulin, and Hypurin neutral, etc.
What type of insulin is ReliOn R insulin?
ReliOn R is an intermediate-acting insulin. It starts acting within 2 – 4 hours of injection and is a safe and effective and relatively low-cost option among various insulin brands present in the market.
Lantus insulin vs Humulin, how are they different?
Humulin is a fast-acting form of insulin and is typically used for managing mealtime surge in blood sugar. Lantus on the other hand is a long-acting insulin and its effect on the body is slow and steady for up to 24 hours post injection.
Can I substitute Novolin 70 30 for Humulin 70 30?
Yes, they can be used interchangeably as both Novolin and Humulin are the two different brands of insulin NPH.
References:
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English