Last updated on August 1st, 2022
Glycosuria is a condition in which blood glucose passes into the urine. Usually, kidneys absorb blood glucose from any passing fluid into the blood vessels. In glycosuria, kidneys fail to remove enough blood glucose off the urine. This occurs in presence of abnormally high level of sugar in blood (hyperglycemia). Often, glycosuria develops even in the presence of normal or low blood glucose levels. In such conditions, it’s known as renal glycosuria.
Glycosuria happens in conditions like diabetes. People are unaware that they have glycosuria until they go for urine test. This condition occurs in the presence of following in the urine:
- glucose
- lactose
- fructose
- galactose.
The body regulates the sugar levels to maintain a steady balance. Excessive sugar may damage the body organs and nerves. Yet, the body requires enough glucose for energy. A small quantity of sugar in urine is normal. Glycosuria occurs when a random urine sample shows values above 0.25mg/ml. Excessively raised sugar levels can be a cause. Also, a problem with the kidney filters can be a reason for this.

Causes of Glycosuria
There are 3 major causes of glycosuria:
- Medical problems indicating a lack of usage or production of insulin.
- Problems with the kidney. Showing a damage in the tubules or other kidney defects.
- Consumption of more sugars than the body processes at once
Glycosuria may occur due to an underlying condition such as diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common reason for glycosuria. In the presence of glycosuria, the body’s insulin fails to work properly. Insulin can’t move blood glucose into the body cells efficiently. This may cause passage of blood glucose in the urine instead. Also, the body fails to produce enough insulin to stabilize the sugar levels. Any excess glucose then passes out via urine.

Glycosuria in Diabetes
Diabetes is when the body fails to make enough insulin or use insulin. Insulin controls the amount of glucose present in the blood.
There are two forms of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes. It is an autoimmune disorder. The immune system damages the beta cells responsible for producing insulin. Type 1 diabetes develops in children or teenagers usually.
- Type 2 diabetes. Here, the body becomes resistant to insulin. And, thus fails to respond to the hormone. This gives rise to problems while using glucose. Obesity and weight gain are most common factors of type 2 diabetes. It develops later in life; however, overweight children may also get type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes
Glycosuria may also occur in presence of gestational diabetes during pregnancy. It occurs when hormones coming from the baby’s placenta prevent the insulin to control sugar levels. This may abnormally increase the blood glucose levels. Gestational diabetes is preventable, although.
High sugar levels during pregnancy might result in several problems:
- Baby grows too big
- A female requires a C section
- High blood pressure
- High blood glucose in the baby
- Risk of cardiovascular problems and type 2 diabetes after pregnancy
A doctor may perform in-office urine tests to check for glycosuria. He or she may prescribe another test around the 24-28 week. In this test, a female has to have a glucose drink. And, then give the blood sample. The doctor may do the blood test earlier in cases of high glycosuria.
Renal Glycosuria
Renal glycosuria is a rarer type of glycosuria. In this, the kidney’s tubules (filters) fail to filter blood glucose out of the urine. A mutation in a specific gene causes this problem. Renal glycosuria generally doesn’t have any signs. And there is no need of any treatment.
Fanconi Syndrome and Glycosuria
Fanconi syndrome refers to a kidney defect causing sugar absorption problems. Many factors may cause this:
- Medications
- Kidney transplant
- Lack of vitamin D
- Heavy metal exposure
Other genetic conditions may also be responsible for this:
- Lowe syndrome
- Cystinosis
- Wilson disease
- Dent disease
Alimentary Glycosuria
It may occur when a person consumes a lot of carbs. Blood sugar levels become irregularly high after consuming. The sugar passes in the urine and the levels take longer to stabilize. It is a temporary condition in healthy individuals. However, it may be a symptom of renal glycosuria. Also, it may occur in diabetic people.
Hyperthyroidism
Another cause of glycosuria is increased production of thyroid hormones in the blood. This may cause poor absorption of sugar from the filtrate. And, hence sugar passes into the urine.
Medications
Medications that reduce the glucose absorption in the kidneys may induce glycosuria. These medicines work on the tubules. These can be Canagliflozin, or Dapagliflozin. These medicines may slightly enhance the risk of UTIs. These belong to the class of “SGLT2 inhibitors”. And, are known to cause the kidneys to excrete more sugar via urine.
- Farxiga (dapagliflozin): Common side-effects can be yeast infections, UTIs, urinating more often, nausea, back pain, increased cholesterol levels.
- Invokana (canagliflozin): Common side-effects are the same as above.
Yeast infections most commonly occur with these medicines. Yet, particularly when the blood sugar levels are intensely high (more than 250 mg/dL). It indicates a significant amount of glucose passing via urine. Having a lot of water while using these drugs is vital. This helps in transporting that extra glucose.
Liver problems
Liver cirrhosis may affect the carb metabolism. This causes high sugar levels in the blood. These high sugar levels exceed the threshold. This results in excretion of sugar into the urine.
Glycosuria Signs
A person may remain unaware of glycosuria until a urine test is done. Few types such as renal and gestational glycosuria do not present signs. With time, if is left untreated, it may cause symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Urination more often
- Weight loss
- Feeling very thirsty
- Feeling ill
Glycosuria Diagnosis
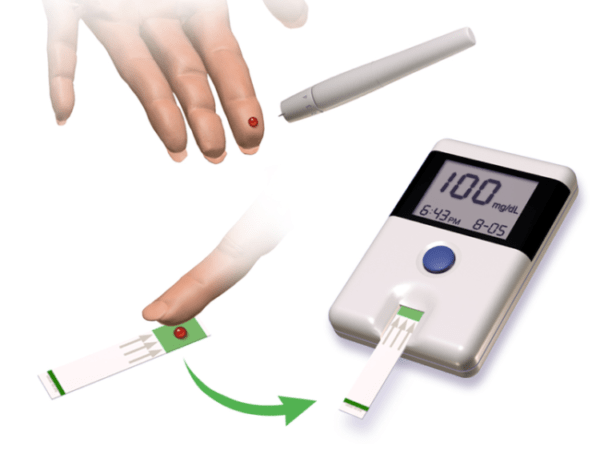
Diagnosis can be done in several ways. Urinalysis is the most common one.
In this test, a doctor asks a person to urinate on a test strip. Then, it is sent to a lab for testing. The technician determines whether the urine sugar levels indicate glycosuria. A person might have glycosuria: if sugar amount in the urine is above 180 mg/dL in a single day.
A doctor might also order blood tests. These check the levels of blood sugar. Normal blood glucose levels lie between 70–140 mg/dL. This depends on whether a person has consumed recently or whether is diabetic.
A doctor performs a glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test if:
- the blood glucose levels are high
- diabetes diagnosis has not been done previously.
This test gives data on the glucose levels for the past few months.
Glycosuria Treatment
The glycosuria treatment depends on the cause. A best diabetes management is seen with lifestyle changes and medicines. Treatments may be:
- Insulin
- Metformin: medicine which allows the body to react better to insulin.
- Sulfonylureas: helps the body make more insulin.
- ACE inhibitors
- Statins
- Diet changes: developing a diet plan that offers sufficient nutrients. Also, reduces the intake of sugars or fats. This might mean consuming more fruits, veggies, and whole grains.
- Exercise: at least half an hour of physical activity each day.
- Anti-glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor antagonists
Also, a regular monitoring of the glucose levels is must. This gives a better understanding of how the body responds to foods, activities, or therapies. Not every person with glycosuria is ill or requires treatment. In case of signs of blood glucose problems, discuss with a doctor.
If glycosuria associates with diabetic kidney disease, a person must speak to a nephrology team. Glycosuria in diabetics might also not be due to medicines. This might indicate that the glucose levels are very high or kidneys are battling. And, a proper intervention is essential. Ask a doctor to add in a urinalysis at the next check-up!
Also, if you wish to know more glycosuria and diabetes, speak to a diabetes educator. Any person can take help from diabetes reversal plans such as Breathe Well-being. This helps a diabetic to feel motivated again. Breathe Well-being’s Diabetes Reversal program is a holistic care program for diabetes. This reversal plan helps maintain healthy glucose levels by working upon diet, fitness, or exercise, stress lowering approaches. So, hurry and get benefits from our cost-effective package by visiting our website.
So, no more medications, no more insulin, no more pain, or risk of complications. Salvage your overall health with our natural reversal plan.
FAQs:
How does sugar influence urine output?
When there’s an excess of glucose in the blood, kidney work harder to remove it. This occurs if a person is diabetic. And, forces them to produce more urine.
How does stress result in glycosuria?
High blood sugar levels exceed the renal threshold. This causes the excretion of sugar in urine. Emotions resulting in glycosuria can be:
- Fear
- Anger
- Anxiety
These may release the hormone, adrenaline.
Can I have sugar in my urine even if I am not diabetic?
Non-diabetics may notice high glucose levels in their urine in these kidney problems:
- chronic kidney disease
- after a renal transplant.
Does sugar in urine show kidney damage?
High blood glucose is the primary cause of sugar in urine. This might show some potentially serious conditions. Glucose in urine directs conditions such as:
- Diabetes
- kidney disease
- hereditary defects
Glucose in urine needs an immediate and urgent medical help.
Is there any difference between glycosuria and Glucosuria?
Glycosuria means the presence of reducing sugars in the urine. These can be glucose, galactose, lactose, fructose, etc. Glucosuria defines the presence of sugar in the urine. And, it is the most common form of glycosuria.
Does glycosuria result in dehydration?
Glycosuria causes too much water loss into the urine. This brings about dehydration, a process referred to as osmotic diuresis.
References:
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English